Phenylethylene glycol 1-phenyl-2-ethanediol
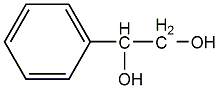

Structural formula
| Business number | 026H |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H10O2 |
| Molecular weight | 138.16 |
| label |
1-phenyl-1,2-ethylene glycol, 1,2-Dihydroxy-1-phenylethane, Phenyl-1,2-ethylene glycol, 1-Phenylethylene glycol, 1,2-Dihydroxyethylbenzene, C6H5CH(OH)CH2OH |
Numbering system
CAS number:93-56-1
MDL number:MFCD00003546
EINECS number:202-258-1
RTECS number:KI2500000
BRN number:1306723
PubChem number:24887135
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: white needle-like crystals.
2. Density (g/mL,25/4℃):
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL,AIR=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC):69 -70
5. Boiling point (ºC,Normal pressure):272-274
6. Boiling point (ºC,5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flashpoint (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific optical rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa,25ºC): Undetermined
17. Explosion Upper limit (%,V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%,V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Easily soluble in water, alcohol, ether and benzene, slightly soluble in petroleum ether, but easily soluble in hot petroleum ether.
Toxicological data
None
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index:38.87
2. Molar volume (m3/ mol):118.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 315.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 51.4
5. Polarizability(10-24cm3):15.41
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 40.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 87.3
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
None
Storage method
This product should be kept sealed.
Synthesis method
The reaction between styrene and bromine produces 1,2-dibromophenylethane, which is then hydrolyzed to obtain phenylglycol. Add styrene to petroleum ether, add bromine dropwise under cooling, control the temperature below 15°C, stir for 1 hour after adding, filter out the white crystals of 1,2-dibromophenylethane, and mix them with water and potassium carbonate. Reflux for 20h. Cool, separate the upper oil layer, saturate the water layer with potassium carbonate and precipitate the oil layer. Separate the oil layer. The aqueous layer was extracted with benzene. The extract is combined with the oil layer, and benzene is recovered after drying, and then phenylglycol is distilled off under reduced pressure.
Purpose
Used in organic synthesis.
T-FAMILY: ‘Arial’,’sans-serif’; mso-fareast-font-family: Arial”>3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K):315.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 51.4
5. Polarizability(10-24cm3):15.41
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 40.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 87.3
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
None
Storage method
This product should be kept sealed.
Synthesis method
The reaction between styrene and bromine produces 1,2-dibromophenylethane, which is then hydrolyzed to obtain phenylglycol. Add styrene to petroleum ether, add bromine dropwise under cooling, control the temperature below 15°C, stir for 1 hour after adding, filter out the white crystals of 1,2-dibromophenylethane, and mix them with water and potassium carbonate. Reflux for 20h. Cool, separate the upper oil layer, saturate the water layer with potassium carbonate and precipitate the oil layer. Separate the oil layer. The aqueous layer was extracted with benzene. The extract is combined with the oil layer, and benzene is recovered after drying, and then phenylglycol is distilled off under reduced pressure.
Purpose
Used in organic synthesis.
