Pyrene Pyrene
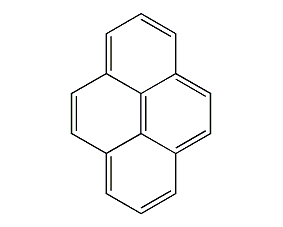

Structural formula
| Business number | 03LW |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C16H10 |
| Molecular weight | 202 |
| label |
rylene, Benzo[DEF]phenanthrene, Benzo[def]phenanthrene, aromatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:129-00-0
MDL number:MFCD00004136
EINECS number:204-927-3
RTECS number:UR2450000
BRN number:1307225
PubChem number:24888024
Physical property data
1. Properties: Monoclinic prismatic or flaky crystals, the pure product is colorless, and when it contains tetracene, it turns yellow. Both solid and solution have slight blue fluorescence.
2. Relative density (d234) : 1.271
3. Melting point (℃): 150.2
4. Boiling point (ºC): 4045. Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol and ether. 6. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.096150.2
7. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -7951.0
8. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 225.7
9. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 402.26
10. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): 328.0
11. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 204.20
12. Crystal phase standard combustion heat ( Enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -7875.77
13. Crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1) : 125.49
14. Crystal phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 224.89
15 . The standard free energy of formation of the crystal phase (kJ·mol-1): 280.4
16. The standard hot melt of the crystal phase (J·mol-1·K-1): 234
Toxicological data
This product is toxic. In acute poisoning, it first causes excitement, which then turns to depression, spasm, quadriparesis, and irritation of the eye and upper respiratory tract mucosa. The LD50 of rats is 0.17mg/L, and the LD50 of mice is 0.8g/kg.
Ecological data
General remarks
Water hazard class 3 (German regulations) (self-assessment via list) This substance is extremely hazardous to water.
Do not allow undiluted or large amounts of product, even in small amounts, to come into contact with groundwater, waterways, or sewage systems.
Even extremely small amounts of product seeping into the ground can pose a hazard to drinking water.
Do not discharge materials into the surrounding environment without government permission.
Molecular structure data
5. Molecular property data:
1. Molar refractive index: 72.46
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 161.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 449.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 59.4
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 28.72
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 16
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 217
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. This product is toxic. In acute poisoning, it first causes excitement, which then turns to depression, spasm, quadriparesis, and irritation of the eye and upper respiratory tract mucosa. The LD50 of rats is 0.17mg/L, and the LD50 of mice is 0.8g/kg. Operators should wear protective equipment.
2. Exist in oriental tobacco leaves and mainstream smoke.
Storage method
Storage
Sealed and stored
Packed in plastic bags, they are dangerous goods and should be transported according to dangerous goods regulations.
Synthesis method
The content in high-temperature tar is about 1.2% to 1.8%.
1. Use dianthracene oil as raw material, vacuum distillation, extraction, recrystallization and purification.
2. Use the residue of distilled anthracene oil above 360℃ as raw material, rectify and cut the pyrene fraction, use benzene as the solvent, wash with concentrated sulfuric acid to remove the base and unsaturated compounds, and then recrystallize with solvent oil to obtain pure Taste.
3. Tobacco: OR, 26.
Purpose
Organic synthesis. Organic synthetic raw materials can be oxidized to produce 1,4,5,8-naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid, which is used in dyes, synthetic resins and engineering plastics; after oxidation, it can be used to produce vat dyes. Orange GR and many other dyes. It can also be used to make pesticides, plasticizers, etc.
