Squalene Squalene
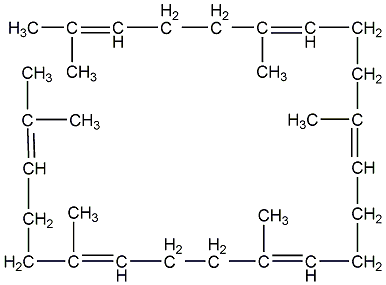

Structural formula
| Business number | 032N |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C30H50 |
| Molecular weight | 410.72 |
| label |
spinachene, 2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22-tetracosahexene, 2,6,10,15,19,23-Hexamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22-tetracosahexaene, Spinacene, Supraene, aliphatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:111-02-4
MDL number:MFCD00008912
EINECS number:1728919
RTECS number:KB6010000
BRN number:1728919
PubChem number:24899564
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless or slightly yellow oily clear liquid with a faint pleasant odor.
2. Density (g/mL, 20℃): 0.858
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): -4.8
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 421.3
6. Boiling point (ºC, kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index(n20D): 1.499
8 . Flash point (ºC): 200
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/ mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water ( Log value of the partition coefficient (octanol/water): Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/ V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Almost insoluble in water, soluble in ether, petroleum ether, acetone, etc., slightly soluble in ethanol and glacial acetic acid.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Mouse oral LD5O: 5gm/kg
Ecological data
This substance is slightly harmful to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
5. Molecular property data:
1. Molar refractive index: 140.743
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 484.2
3. Isotonic volume (90.2K): 1126.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 29.2
5. Dielectric constant (F/m ): 3.06
6. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 55.67
Compute chemical data
1�� Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 11.6
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 15
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 30
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 578
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 4
14. Number of uncertain stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It does not decompose under normal temperature and pressure. Contact with strong oxidants is prohibited.
2. Exist in oriental tobacco leaves and smoke.
3. Found in large amounts in shark liver oil.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
Method 1. Use shark liver oil as raw material
Distill the shark liver oil under reduced pressure to obtain 3.5% of the initial fraction containing squalane, remove it, and leave the residual oil (96.5%) at 533.28-666.61Pa (4-5mmHg ) is distilled to 242°C with almost no distillate. 1450g of this distillate was first treated with sodium hydroxide to remove free acid, and then distilled on metallic sodium under a pressure of 666.61Pa (5mmHg) to obtain the finished product of squalene. 1383g of this distillate was fractionated four times under a pressure of 1.333kPa (10mmHg), and the first fraction was distilled off at 282°C in the oil bath.
Shark liver oil [deacidification, vacuum distillation] → [vacuum distillation] → [sodium] squalene finished product
Method 2, using shark liver as raw material
Preparation of concentrated liquid, taking shark Liver, washed and minced, steamed with steam at 100°C for 4 hours in a double-layer boiler, and then extracted to obtain an extract. Concentrate to obtain a concentrated liquid.
Shark liver (crushed) [100℃ steam, 4h] → Extract solution [Concentrated] → Concentrated solution
Preparation of finished squalene product: Leave the concentrated solution for one day and night, cool naturally, and then extract the supernatant. Add acidic clay and stir, leave it for a day and night, remove the precipitate, and obtain a supernatant liquid. The supernatant liquid is refined once, and filtered with No. 2 filter paper to obtain the finished product of squalene.
Concentrate → Supernatant [acid clay] → Supernatant [Refined] → Finished fish squalene
Method 3. Use shark liver as raw material
Preparation of crude oil Take 900g fresh Frozen whale shark liver, remove the blood water, cut into pieces, put in 3 times (300g each time) in a high-speed masher, add 250ml distilled water to each tissue, homogenize for 2 minutes, pour into a 2000ml beaker, and place in a water temperature of about 80°C Heat, and use 1 mol/L sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH of the liver homogenate to about 9, stir continuously, heat for about 1 hour, centrifuge while hot (3000r/min, 20min), absorb the yellow oily substance in the upper layer, and use saturated sodium chloride solution Wash 2-3 times, then wash with distilled water until the Ph is neutral, and approximately 300ml of crude oil is obtained.
Shark liver [mashed] → homogenate [saponification, separation] → [NaOH, 80℃] yellow oil [NaCl, H2O] → crude oil
Refining of squalene, take 1 portion of 170ml The crude product is placed in a vacuum distillation flask, heated in a silicone oil bath, and distilled under reduced pressure. When the internal temperature is 85-140°C and the vacuum degree is 6-1.2Pa, the first fraction begins to appear, which is a yellow oily substance, about 40ml. When the internal temperature rises to 190-206°C and the vacuum degree is 0.8-0.4Pa, collect the second fraction, which is a light yellow oil, about 78 ml.
Put the oily substance of the II fraction into a vacuum distillation flask equipped with a fractionating column and perform vacuum distillation again. When the internal temperature is 190°C and the vacuum degree is 0.53Pa, a light yellow oily substance begins to appear, about 20ml. When the internal temperature rises to 195-200°C and the vacuum degree is 0.4-0.13Pa, collect a colorless and transparent oily substance, about 35ml, which is the refined squalene product.
Crude oil [silicone oil bath] → [190-206℃, 0.8-0.4Pa] light yellow oil [concentration under reduced pressure] → [195-200℃, 0.4-0.13Pa] refined squalene.
Method 4:
Tobacco: OR, 57.
Method 5:
There are trace amounts of isomers in squalene obtained from flue gas.
Purpose
1. Nutritional medicine. Oral use to treat high and low blood pressure, anemia, diabetes, liver cirrhosis, cancer, constipation, dental decay; external use to treat tonsillitis, wheezing, bronchitis, colds, tuberculosis, rhinitis, gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, gallbladder and bladder stones. , rheumatism, neuralgia, etc.
2. Cholesterol biological intermediates.
3. Used as fungicides, intermediates in drug production, aromatics, etc.
