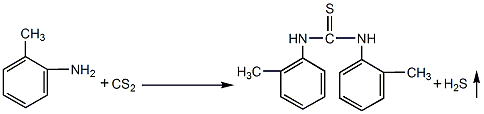
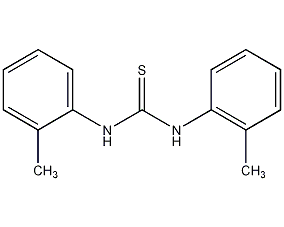
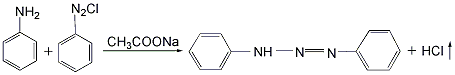
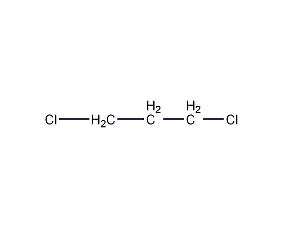
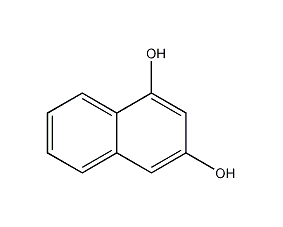
1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone
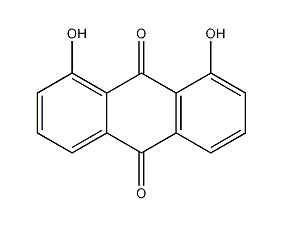

Structural formula
| Business number | 038W |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C14H8O4 |
| Molecular weight | 240.21 |
| label |
Chrysazine, Danthron, Quinones |
Numbering system
CAS number:117-10-2
MDL number:MFCD00001211
EINECS number:204-173-5
RTECS number:CB6650000
BRN number:2054727
PubChem number:24893346
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: Yellow, red-yellow or red needle-like or flake crystals.
2. Density (g/mL,20℃) : Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL,Air =1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 191~193, can be sublimated.
5. Boiling point (ºC,normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, KPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flashpoint (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (octanol/Log value of the partition coefficient for water: undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%,V/V): Undetermined
Molar volume (m3/mol): 155.9
3、 Isotonic specific volume (90.2K) :465.2
4、 Surface Tension (dyne/cm):79.2
5、 Polarizability (10-24cm3):24.74
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 14
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 74.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 18
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 346
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Stable at normal temperature and pressure, avoid contact with Strong oxidizing agentContact.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and water sources. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
It is produced by disulfonation or dinitration of anthraquinone.
Purpose
Used as dyes and pharmaceutical intermediates.
“>
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 14
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 74.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 18
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 346
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Stable at normal temperature and pressure, avoid contact with Strong oxidizing agentContact.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and water sources. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
It is produced by disulfonation or dinitration of anthraquinone.
Purpose
Used as dyes and pharmaceutical intermediates.