1,4,5,8-naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid 1,4,5,8-naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid
Structural formula
| Business number | 03LV |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C14H8O8 |
| Molecular weight | 304.21 |
| label |
naphthalene tetracarboxylic acid, 1,4,5,8-naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid, Naphthalene-1,4,5,8-tetracarboxylic acid, aromatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:128-97-2
MDL number:MFCD00004012
EINECS number:None
RTECS number:QK3690000
BRN number:None
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: White crystal
2. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water and hot acetic acid, soluble in acetone aqueous solution, very slightly soluble in benzene, chloroform, carbon disulfide and ethanol.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD5O: 7500mg/kg
Mouse oral LD5O: 3800mg/kg
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 71.81
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 173.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 559.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 107.8
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 28.46
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 4
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 8
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 149
7. Number of heavy atoms: 22
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 423
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Low toxicity. It has a slightly sour smell and will not harm human health as long as the working environment is well ventilated. In the process of producing naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid, whether pyrene fraction or acenaphthene is used as raw material, they are toxic substances.
Storage method
None yet
Synthesis method
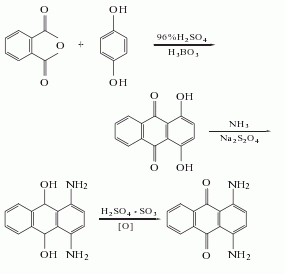
1. Pyrene method: Using pyrene as raw material, it is obtained through chlorination and oxidation.
2. Acenaphthene method This method includes propylene glycol method and carbamoyl chloride method.
(1) Propylene chloride method: Dissolve the cyanoacetic acid amide obtained by cyanidation, ammoniation and dehydration of chloroacetic acid in chlorobenzene, react with phosphorus pentachloride to obtain propylene chloride, theoretically The yield is 77%. Add malonite and an equal amount of acenaphthene to chlorobenzene, add aluminum trichloride, and pass in hydrogen chloride at the same time, and heat the reaction to obtain diiminoketone with a theoretical yield of 89%. Oxidize the diiminoketone with sodium hypochlorite and potassium permanganate to obtain 1,4,5,8-naphthalenetetracarboxylic acid. The theoretical yield is 51.8%.
(2) Carbamoyl chloride method In the presence of aluminum trichloride, acenaphthene and carbamoyl chloride are heated in chlorobenzene to react. reaction�First acidify with concentrated hydrochloric acid, and then hydrolyze with sodium hydroxide to obtain 5,6-acenaphthylenedicarboxylic acid, with a yield of 63%. 5,6-acenaphthylenedicarboxylic acid is further oxidized to obtain 1,4,5,8-acenaphthylenetetracarboxylic acid, with a yield of 60%.
Purpose
Dye intermediates. It can be used to produce dyes such as vat orange GR. The plastics industry is used to manufacture new resins—polyimide and TNM polymers—that have good insulation, radiation resistance, and can withstand high temperatures (400°C).