1,3-Butaneiol 1,3-Butaneiol
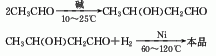
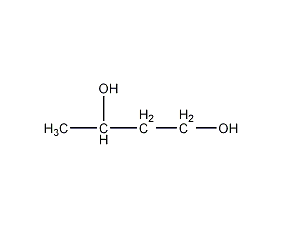
Structural formula
| Business number | 02VY |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H10O2 |
| Molecular weight | 90.12 |
| label |
(±)-1,3-butanediol, 1,3-Dihydroxybutane, 1,3-Butylene glycol, 1,3-Dihydroxybutane, β-Butylene glycol, D, softener, alcohol solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:107-88-0
MDL number:MFCD00004554
EINECS number:203-529-7
RTECS number:EK0440000
BRN number:1731276
PubChem number:24858732
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless viscous liquid with bitter and sweet taste.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa): 203~204
3. Boiling point (ºC, 1.60kPa): 108
4. Boiling point (ºC ,1.33kPa): 98
5. Melting point (ºC): -54
6. Relative density (g/mL, 20/4ºC): 1.0053
7. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 3.2
8. Refractive index (n20ºC): 1.441
9. Refractive index (n25ºC): 1.439
10. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 130.3
11. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 103.9
12. Viscosity (mPa· s, 35ºC): 89
13. Flash point (ºC, open): 121
14. Fire point (ºC): 392.8
15. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 58.49
16. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, liquid): 2491.2
17. Vapor pressure (kPa, 74ºC): 0.067
18. Critical temperature (ºC): 290.8
19. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.89
20. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): 1.9
21. Solubility: Miscible with water, ethanol, acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, and dibutyl phthalate. Insoluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons, benzene, toluene, carbon tetrachloride, phenol, 2-aminoethanol, mineral oil, cottonseed oil, etc.
22. Boiling point (ºC): 207
23. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.295
24 . Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 305
25. Critical compression factor: 0.217
26. Eccentricity factor: 1.146
27. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 26.974
28. van van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 8.310×109
29. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 56.990
30. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2570.0
31. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -433.2
32. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2502.2
33. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -501.0
34. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol -1·K-1): 236.4
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation
Standard Draize test: rabbit, skin contact: 500mg/24H, severity of reaction: mild.
Standard Draize test: Rabbit, eye contact: 500 mg, severity of reaction: mild.
Standard Draize test: rabbit, eye contact: 500mg/24H, severity of reaction: mild.
2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 18610mg/kg; rat subcutaneous LD50: 20mg/kg; The mouse through the abdominal cavity LC50: 10276mg/kg;
Rabbit contacts LD50: > 20 mg/kg; Guinea pigs LD50: 11mg/kg;
3, reproductive toxicity: rats Oral TDLo: 42360mg/kg (female rats are pregnant for 6-15 days);
4. The toxicity is similar to that of glycerol, which is slightly toxic and has no irritation to human mucous membranes and skin. Animals show symptoms during acute poisoning. Deep anesthesia.
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 23.60
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 89.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 222.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 37.1
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 9.35
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.4
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
p>
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 40.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 28.7
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with strong oxidants, strong acids, acid chlorides, and acid anhydrides. Flammable liquids. It is hygroscopic and non-corrosive to metals.
2. The toxicity to higher animals is very low, lower than 1,4-butanediol. Rat oral LD502.8g/kg. In high doses, it has an anesthetic effect and has a certain inhibitory effect on the central nervous system. No obvious irritation to skin and mucous membranes.
3. Found in tobacco leaves.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, etc., and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
2.Ordinary storage and transportation methods can be used. See glycerol.
Synthesis method
1. It is obtained by aldol condensation of acetaldehyde in alkaline water to 3-methylbutyraldehyde, and then hydrogenated and reduced.
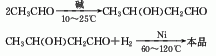
2. From propylene and formaldehyde in the presence of sulfuric acid formed by condensation.
3.Use acetaldehyde condensation method. In the presence of sodium hydroxide, acetaldehyde is condensed to obtain butyraldehyde, and nickel is used as a catalyst. The crude product is obtained by hydrogenation, which is then cooled, separated from nickel, and distilled under reduced pressure.
Purpose
1. Used to prepare polyester resin, polyurethane resin, plasticizer, ink, etc. Also used as a wetting agent and softener for textiles, paper and tobacco.
2.Organic synthesis intermediates. Used to synthesize plastic additives, food additives, etc. Used as industrial solvent. It is used as a moisturizer in cosmetics and has good antibacterial effects. Can be used in various lotions, creams, toothpastes, etc. It is a good additive for various essential oils and dyes.