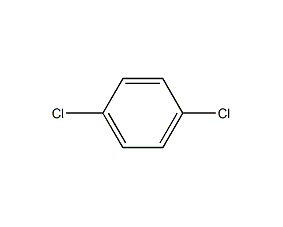
1,2-Epoxybutane 1,2-Epoxybutane


Structural formula
| Business number | 02U3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H8O |
| Molecular weight | 72.11 |
| label |
1,2-butane oxide, butylene oxide, 1,2-Butane oxidation, Epoxy butane, reactive diluent, antioxidants, Surfactant, gasoline additives |
Numbering system
CAS number:106-88-7
MDL number:MFCD00005153
EINECS number:203-438-2
RTECS number:EK3675000
BRN number:102411
PubChem number:24851904
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless liquid with an ether-like odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -150[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 63.3[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.83[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.2[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 18.62 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2552.3[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.39[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.416[9]
10. Flash point (℃): -22 (CC )[10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 439[11]
12. Explosion upper limit ( %): 18.3[12]
13. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.5[13]
14. Dissolution Properties: Soluble in water, miscible in most organic solvents. [14]
15. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 0.8308
16. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ· mol-1): -2548.47
17. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -168.87
18. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 144.7
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[15] LD50: 500mg/kg (rat oral); 2100mg/kg (rabbit dermal )
2. Irritation[16] Rabbit transdermal: 500mg (24h), mild irritation.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity[17] Rats, guinea pigs and rabbits repeatedly inhaled 1.18g/m 3, 7 hours a day, can be tolerated for a long time.
4. Mutagenicity[18] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 3333μg/dish. DNA damage: E. coli 1μmol/L. Sister chromatid exchange: hamster lung 2500 μmol/L.
5. Carcinogenicity[19] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G2B, suspected human carcinogen.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[20]
LC50: 72mg/L (96h) (Bluegill Fish, static);
52.9mg/L (96h) (blackheaded beetleFish, dynamic);
52~72mg/L (96h) (red perch)
EC50: >530mg/L (48h) (water flea)
2. Biodegradability[21]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 168~310
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 627~2688
3. Non-biodegradability[22]
The half-life of photooxidation in water (h): 12000~480000
The half-life of photooxidation in air (h): 30.5~350
First-level hydrolysis Half-life (h): 310
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 20.15
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 81.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 188.8
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 28.3
5. Polarizability: 7.99
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.8
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 12.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 34.6
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: Highly reactive, capable of ring-opening reactions with a variety of reagents. For example, it reacts with water, ethanol, polyols, mercaptans, phenol, ammonia, amines, acids and other compounds containing active hydrogen atoms to open the ring to generate various compounds. Hydroxy acids are generated during oxidation. When catalytic reduction is performed using nickel and platinum as catalysts, 1-butanol is generated. Rearranges to carbonyl compounds when heated or heated with inorganic acids. It can be polymerized alone or copolymerized with other alkyl epoxy compounds to form polyether.
2. Stability[23] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[24] Strong oxidants, acids
4. Conditions to avoid contact [25] Heating, contact with air
5. Hazards of aggregation[26] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[27] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37℃. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. It should not be stored for a long time to avoid deterioration. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
In industry, butylene oxide comes from the recovery of by-products of propylene oxide production. In the process of producing ethylene oxide and propylene oxide through hypochlorous acidification of cracked tail gas, the propylene oxide tower bottom liquid can be obtained. It contains 74.6% butylene oxide, 16.7% propylene oxide, 0.7% ethylene oxide, 3.1% water, and a small amount of high boiling matter. Through distillation, collect the 50-70°C fraction from the tower, remove the water after condensation, and obtain the 1,2-epoxybutane finished product with a content of approximately 87%. If higher purity is required, further fractionation can be performed.
Purpose
1. This product is used as a reactive diluent for epoxy resin and can also be used as a diluent for nitrocellulose paint instead of acetone. Also used in the manufacture of intermediates and polymers, such as the production of 1,2-butanediol. This product is also a standard for chromatographic analysis.
2. Used as an antioxidant for chlorine-containing compounds such as trichlorethylene. When manufacturing vinyl chloride and its copolymers, adding 0.25% to 0.5% of 1,2-epoxybutane can effectively control the impact of container corrosion on the color and performance of the resin. Others are used in the manufacture of butanolamine, surfactants, and gasoline additives.
3. Used as solvents, stabilizers for chlorinated solvents, and intermediates in organic synthesis. [28]