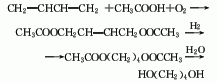Structural formula
| Business number |
031W |
| Molecular formula |
C4H10O2 |
| Molecular weight |
90.12 |
| label |
Ethylene glycol dimethyl ether,
1,2-Dimethoxyethane,
1,2-dimethoxyhexane,
1,2-Dimethylethane,
Ethylene glycol dimethyl ether,
1,2-Ethanediol dimethyl ether,
Dimethylglycol,
Ethylene glycol dimethyl ether,
Monoglyme,
paint stripper,
thinner,
Ether and acetal solvents
|
Numbering system
CAS number:110-71-4
MDL number:MFCD00008502
EINECS number:203-794-9
RTECS number:KI1451000
BRN number:1209237
PubChem number:24855712
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with slight ether smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -58[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 82~83[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.87 (20℃)[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.11[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 6.40 (20℃)[6 ]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2521.2[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 263 [8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.87[9]
10. Octanol/water distribution Coefficient: -0.21[10]
11. Flash point (℃): -2 (CC)[11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 202[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 18.7[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.9[14]
15. Solubility: soluble in water, soluble in ethanol and hydrocarbons. [15]
16. Refractive index (n20ºC): 1.3796
17. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 1.1
18. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol): 28.14
19. Heat of fusion (KJ/kg): 139.4
20. Heat of formation (KJ/mol): 491.95
21. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): 2520.82
22. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), constant pressure): 1.83
23. Conductivity (S/m, 25ºC): 0.47×10-7
24. Vapor pressure (kPa, 20ºC): 6.40
25. Relative Density (20℃, 4℃): 0.8665
26. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 0.855630
27. Critical density ( g·cm-3): 0.293
28. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 308
29. Critical compression factor: 0.269
30. Eccentricity factor: 0.346
31. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3
sup>)0.5: 17.732
32. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 8.140 ×109
33. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 55.200
34. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1)���-2662.95
35. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -340.24
36. Liquid phase standard combustion Heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2626.65
37. The liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -376.64
38. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 186.5
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Mouse oral LC50: 3200mg/kg; Rat oral LD50: >5000mg/kg; Rabbit oral LD50: 320mg/kg; Rat oral LDL0: 1000mg/kg; Rat Skin LD50: 5370mg/kg; rabbit skin LDL0: 2000mg/kg; rat inhalation LDL0: 63mg/m3/6H
2. It is of low toxicity by inhalation and oral administration. Inhaling high-concentration vapor can cause damage to the lungs, liver, kidneys and other organs.
3. Acute toxicity [16] LD50: 775mg/kg (rat oral)
Ecological data
This substance is slightly harmful to water bodies. Do not let this product come into contact with groundwater, waterways or sewage systems.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 24.07
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 1107.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 230.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 21.3
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 9.54
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 18.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 17.5
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: stable in nature and difficult to react. But it can react with hydrogen iodide, hydrogen bromide and concentrated sulfuric acid. In the presence of acidic catalysts, decomposition can occur at high temperatures. Stable to alkali metals below 150°C, metallic sodium can be dried with ethylene glycol dialkyl ether. But it can react with sodium-potassium alloy or potassium. Phenyllithium and butyllithium slightly decompose ethylene glycol dimethyl ether. It does not react with low-activity Grignard reagents such as methylmagnesium chloride under normal conditions, but it decomposes when heated to 150~200°C with highly active reagents such as methylmagnesium iodide. It is stable to alkali metal hydrides and can be used as a stabilizer and refining agent for lithium aluminum hydride. Peroxide is generated under the action of oxygen, and light and heat promote the generation of peroxide. The generated peroxide is unstable and decomposes into aldehydes, ketones, acids and other impurities.
2. Stability[17] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[18] Strong oxidants, strong acids
4. Conditions to avoid contact [19] Air, light
5. Hazards of aggregation[20] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[21] Usually products contain stabilizers. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C, and the packaging must be sealed and not in contact with air. They should be stored separately from oxidants and acids, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reaction of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and metal sodium; methyl chloride. Reflux ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and metal sodium together until the metal sodium reacts completely, cool the temperature to 45°C, and introduce methyl chloride. After the reaction is completed, perform fractional distillation and collect the 84-85.5°C fraction to obtain the finished product.
Refining method: The testing method for peroxide is the same as that for ether. The peroxides can be removed by refluxing with stannous chloride or by passing through activated alumina. Then add a small amount of metallic sodium to remove trace amounts of moisture. Other refining methods include drying with sodium wire and distilling with lithium aluminum hydride under nitrogen flow. You can also dry it with anhydrous calcium chloride for a few days, filter, add metallic sodium for distillation, or add lithium aluminum hydride to preserve it, and distill it before use.
2. Add metal sodium to ethylene glycol monomethyl ether in small amounts at 60°C while stirring. Control the temperature at 78-81°C. After adding metal sodium, cool down to 45°C. , and then pass in methyl chloride. The reaction formula is:

After the reaction is completed , distill, and collect the 84.5-85.5°C fraction to obtain ethylene glycol dimethyl ether.
3. After drying with sodium wire, add lithium aluminum hydride for distillation in the presence of nitrogen. You can also use anhydrous calcium chloride to dry for several days, filter out the calcium chloride, and then add metallic sodium for distillation, or Add lithium aluminum hydride and let it stand for distillation.
Purpose
1. Used as a solvent for nitrocellulose, resin, etc. and a solvent for preparing alkali metal oxides and borane. Aromatic hydrocarbons such as naphthalene, biphenyl, terphenyl, and anthracene form complexes with sodium in ethylene glycol dimethyl ether. Sodium-naphthalene complex is used for surface treatment when bonding fluorine-containing resins such as polytetrafluoroethylene. Sodium-biphenyl complex is used for the determination of halogens in gasoline. It can also be used to recover acetic acid from dilute acetic acid aqueous solution. It is also used as paint remover, thinner and to increase the viscosity of lubricating oil.
2. Used as solvents, pharmaceutical extraction agents, organic synthesis intermediates, catalysts, and corrosion inhibitors. [22]
Aromatic hydrocarbons form complexes with sodium in ethylene glycol dimethyl ether. Sodium-naphthalene complex is used for surface treatment when bonding fluorine-containing resins such as polytetrafluoroethylene. Sodium-biphenyl complex is used for the determination of halogens in gasoline. It can also be used to recover acetic acid from dilute acetic acid aqueous solution. It is also used as paint remover, thinner and to increase the viscosity of lubricating oil.
2. Used as solvents, pharmaceutical extraction agents, organic synthesis intermediates, catalysts, and corrosion inhibitors. [22]