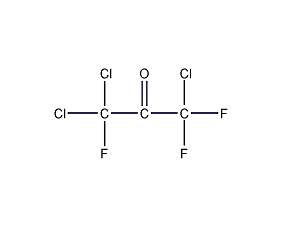
Structural formula
| Business number |
01PR |
| Molecular formula |
C2H2Cl4 |
| Molecular weight |
167.85 |
| label |
Symmetric tetrachloroethane,
Tetrachloroethane,
Acetylene tetrachloride,
sym-Tetra-chloroethane,
CHCl2CHCl2,
pesticides,
herbicide,
special purpose solvents
|
Numbering system
CAS number:79-34-5
MDL number:MFCD00000848
EINECS number:201-197-8
RTECS number:KI8575000
BRN number:969206
PubChem number:24888839
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with chloroform-like odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -43.8[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 146.4[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.60[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 5.79[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 1.33 (32℃)[6]
7. Critical temperature (℃): 388[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.99[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.39[9]
10. Solubility: slightly soluble in water, soluble in acetone, mixed Soluble in ethanol, ether, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, chloroform, etc. [10]
11. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 1.77
12. Specific heat (liquid) (KJ/(kg·K )): 1.122
13. Heat of evaporation (J/g, b.p.): 229.8
14. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, gas): 149.0
15. Heat of combustion (KJ/kg, 18.7ºC, constant volume): 5788.8
16. Conductivity (S/m, 25ºC): 4.5×10-9
17. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K)): 0.1364
18. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1,0~ 30ºC, average): 0.00103
19. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 19.819
20. Lennard-Jones parameter (K): 253.6
21 .Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 20.485
22. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 8.420×109
23. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol -1): 62.520
24. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -194.4
25. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 245.6
26. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 165.4
27. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol -1): -149.0
28. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 355.08
29. Gas phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): -79.4
30. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol -1·K-1):98.99
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[11]
LD50: 200mg/kg (rat oral)
LC50 : 4500mg/m3 (mouse inhalation, 2h)
2. Irritation No data available
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity [12] Causes liver enlargement and tenderness, which may occur Steatosis, necrosis and cirrhosis of the liver, kidneys and myocardium can also be affected.
4. Mutagenicity [13] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 10μg/dish. Sex chromosome deletion and non-disjunction: Aspergillus nidulans 200ppm. DNA inhibition: human HeLa cells 6mmol/L. Sister chromatid exchange: hamster ovary 56mg/L.
5. Carcinogenicity [14] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G3, insufficient evidence of carcinogenicity to humans and animals.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[15]
LC50: 9.23mg/L (48h) (Daphnia magna, static); 21.3mg/ L (96h) (bluegill, static); 20.3mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow, dynamic); 31mg/L (48h) (medaka); 9.02mg/L (96h) (sugar shrimp, Static); 136~146mg/L (96h) (green algae); 6.23~6.44mg/L (96h) (Skeletonema costatum)
2. Biodegradability[16 ]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 672~4320
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 168~672
3. Non-biodegradability[17]
Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 213~2131
First-order hydrolysis half-life (h): 1056
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 30.62
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 107.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 260.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 33.9
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3):12.14
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 26.5
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It has the strongest solubility among chlorinated hydrocarbon solvents and can be completely miscible with various organic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, ether, petroleum ether, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, carbon disulfide, dimethylformamide, etc. dissolve. It can dissolve grease, wax, asphalt, coal tar, camphor, rubber, dyes, ethyl cellulose, nitrocellulose, polyvinyl chloride and other organic substances as well as sulfur, phosphorus, halogen, sodium sulfite and other inorganic substances. Especially regarding the solubility of sulfur, 100g of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane can dissolve 100g of sulfur at 120°C. The solubility in water at 25°C is 0.29%; the solubility of water in 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane is 0.13%. Dry and pure 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane is not highly corrosive to metals, but decomposes in moist air to release highly corrosive hydrogen chloride.
2. In the absence of air, moisture and light, 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane is a stable substance, but when in contact with air, it slowly removes hydrogen chloride and generates trichlorethylene. and trace amounts of phosgene. It gradually decomposes in the presence of moisture to release hydrogen chloride. In the presence of air or oxygen, dichloroacetyl chloride is generated by ultraviolet light irradiation. 1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane is reduced to 1,2-dichloroethylene by treatment with iron, aluminum, zinc and other metals in the presence of boiling water or water vapor. It does not react with chlorine at room temperature. It is chlorinated under ultraviolet light to form hexachloroethane. 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane generates trichlorethylene when thermally cracked in the presence of catalysts such as activated carbon or reacting with milk of lime. Heating with strong alkali generates highly explosive dichloroacetylene.
Storage method
Storage Precautions[18] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, active metal powders, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
Prepared by chlorination of acetylene. The reaction is carried out with tetrachloroethane itself as the solvent (direct reaction between gaseous acetylene and chlorine will explode), and the catalyst is antimony pentachloride or ferric chloride. When ferric chloride catalyst is used, the system is maintained at negative pressure, tetrachloroethane is constantly refluxing, dry acetylene and chlorine are continuously introduced, and the heat of reaction is absorbed and removed by the refluxing tetrachloroethane vapor, and the yield is 97% (for acetylene).
Purpose
1. Due to its high toxicity and strong solubility, in addition to being used as a solvent for special purposes, it is mainly used as a raw material for the manufacture of trichlorethylene and tetrachlorethylene. It is also used in the manufacture of pesticides, herbicides and photographic films.
2. Used as solvent for organic synthesis. [19]