2-Mercaptoethanol 2-Mercaptoethanol
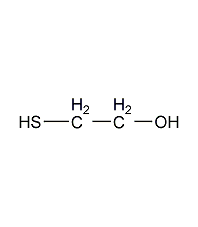
Structural formula
| Business number | 01B5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H6OS |
| Molecular weight | 78.13 |
| label |
Thiol ethanol, β-Mercaptoethanol, 2-Hydroxyethylmercaptan, BME, Thioethylene glycol, Aliphatic sulfur compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:60-24-2
MDL number:MFCD00004890
EINECS number:200-464-6
RTECS number:KL5600000
BRN number:773648
PubChem number:24897085
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless, easy-flowing liquid. Very smelly. The pure product decomposes slowly in the air
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.1143
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1) : Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): Undetermined
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC , 98.69kPa): 157~158
7. Refractive index: 1.4996
8. Flash point (ºC): 73℃
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: in alkaline Easily decomposes in hydrochloric acid. It is freely miscible with water, ethanol, ether and benzene.
Toxicological data
1. Skin or eye irritation: rabbit, skin contact, open irritation test, 10mg/24H; rabbit, eye contact, standard Draize test, 2mg, strong reaction 2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 244mg/kg; Rat inhalation LCLo: 250ppm/8H; mouse oral LD50: 190mg/kg; mouse inhalation LC50: 13200mg/m3; mouse abdominal LD50: 200mg/kg; mouse LD50: 480mg/kg; rabbit, skin contact LD50 : 150uL/kg; guinea pig, skin contact LD50: 300uL/kg3, other multi-dose toxicity: mouse abdominal TDLo: 3220mg/kg/4W-I4, mutagenicity: DNA damageTEST system: microorganisms – not otherwise specified: 10mmol /L; DNA inhibitionTEST system: rodent-mouse liver: 1mmol/L; Micro-testTEST system: rodent-���Mouse cells-not otherwise specified: 100mg/L; indefinite DNA synthesisTEST system: rodent-mouse cells-not otherwise specified: 30mmol/L
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 20.74
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 73.1
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 180.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 37.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.22
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.2
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
p>
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 21.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 10
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Colorless and transparent liquid with a special odor. Freezing point <100℃, boiling point 157-158℃ (98.9kPa), slightly decomposed, 58℃ (2.4kPa), 55℃ (1.73kPa), relative density 1.1143 (20/4℃), refractive index 1.4996, flash point 73℃ . Easily soluble in water, ethanol, ether and other organic solvents, and miscible with benzene in any proportion. Viscosity (20℃) 3.43mPa·s. The pure product decomposes slowly in the air, and its aqueous solution is oxidized into disulfide in the air, and is easily decomposed in alkaline and hydrochloric acid.
2.Thiols molecules, due to the action of -SH ions, can deteriorate the proteins in the skin and mucous membranes, causing the conjunctiva and cornea to become cloudy and even Dissolve. In addition, it generally has a hypnotic effect and can paralyze the central nervous system at high concentrations. Most thiols can be absorbed through the skin. When applied to the skin, they will cause redness due to irritation in the short term. Long-term exposure can cause cancer. However, as the number of carbon atoms in the thiol molecule increases, its toxicity decreases: C1>C2>C3>C4>C5>C6>C7>C8… The equipment should be sealed and the operators should wear protective equipment. See n-Propanethiol.
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored in a cool, dry place away from light.
For packaging, storage and transportation methods, please refer to n-propylmercaptan.
Synthesis method
1. In the early days, it was produced by the reaction of chloroethanol and sodium hydrosulfide. Ethylene oxide and hydrogen sulfide are combined in a molar ratio of 1:3.5, using a strong alkaline anion exchange resin as a catalyst, and react at about 42°C. The obtained crude product has a content of about 52%, and also contains a small amount of thiodiglycol (boiling point 282°C), which is easier to separate and obtain 2-mercaptoethanol. ![]()
2. Dissolve 23 grams of sodium in 400 ml of distilled alcohol, add hydrogen sulfide to make it saturated (6 hours). 44 grams of ethylene oxide and hydrogen sulfide were simultaneously introduced into the mixture within 1 hour, and the temperature was kept below 30°C during this process. After standing overnight, the reaction mixture was poured into water, 60 ml of glacial phosphonic acid was added to neutralize the solution, and extracted with diethyl ether. The ether extract was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, the solvent was evaporated, and the residue was distilled to obtain 24 grams of a fraction with a boiling point of 58°C/12mm, which was identified as β-mercaptoethanol. Also obtained was 29 g of a fraction with a boiling point of 147°C/6mm, which was thiodiglycol.
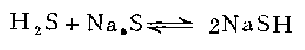
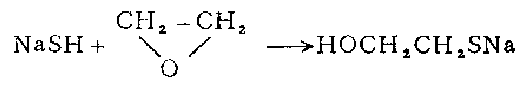
3. in 1 In a three-necked flask, melt 240 grams of sodium sulfide in a water bath and pass in hydrogen sulfide to make it saturated. Add 150 grams of ethanol and pass through hydrogen sulfide to saturate it. Keeping it below 20°C, slowly add 120 g of chloroethanol and leave the reaction mixture at room temperature for 36 hours. Pass hydrogen chloride until the mixture becomes acidic. Filter off the sodium chloride. The filtrate was fractionated under reduced pressure to obtain β-mercaptoethanol, with a yield of 26-30%.
The residue can be further fractionated to obtain thiodiglycol. ![]()
Purpose
1. Study the use of proteins as nitrogen-free hydrogen sulfide reagents. Reducing agent for the fluorescence reaction of o-phthalaldehyde and amino acids in alkaline medium. Prevents the oxidation of certain compounds such as tetrahydrofolate. Solvent. Dye intermediates. flotation agent. Pesticides. Plasticizer.
2. As an organic synthesis intermediate, it is used in the production of pesticides, medicines, dyes, and photographic chemicals. It can also be used as an additive in the rubber, textile, plastic, and coating industries. Polymer grade high-purity mercaptoethanol can be used as a retrieval agent for vinyl chloride, acrylonitrile, etc., as well as a polymerization catalyst, polymer cross-linking agent, and curing agent. This product has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and can be used as an additive in blow-molded containers for food packaging made of acrylonitrile, styrene, and methyl methacrylate ternary resins.
3.Prepare ethylene thioketal, etc. from ketones.
“font-family:Arial;”>Prepare ethylene thioketal, etc. from ketones.