2-Methylvaleraldehyde 2-Methylvaleraldehyde
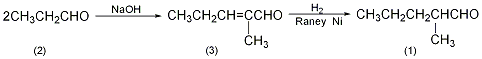
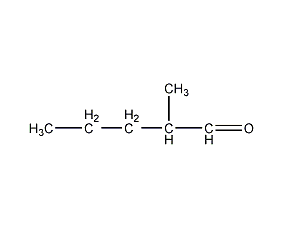
Structural formula
| Business number | 03G7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H12O |
| Molecular weight | 100.06 |
| label |
2-Methyl-1-valeraldehyde, α-Methylvaleraldehyde, 2-Methyl n-valeraldehyde, 2-Methylpentanal, 2-Methyl-n-valeraldehyde, 2-Formylpentane, food additives, Flavor enhancer |
Numbering system
CAS number:123-15-9
MDL number:MFCD00006986
EINECS number:204-605-2
RTECS number:YV4150000
BRN number:1739423
PubChem number:24855648
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid
2. Boiling point (℃): 119~120
3. Relative density (d254) : 0.808
4. Refractive index (n20D): 1.4010 p>
5. Flash point (℃): 16
6. Solubility: soluble in ether, slightly soluble in alcohol, insoluble in water
7. Relative density ( 20℃, 4℃): 0.8080
8. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 0.8034
9. Refractive index at room temperature (n20 ): 1.3997
10. Normal temperature refractive index (n25): 1.3974
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: >3200mg/kg
Rat inhalation LC: >1500ppm/6H
Mouse oral LD50: >3200mg/ kg
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
5. Molecular property data:
1. Molar refractive index: 29.99
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 125.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 377.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 23.9
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 11.88
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.7
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 17.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 50.1
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters.Quantity: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Exist in smoke.
Storage method
None yet
Synthesis method
1. Preparation method: Condensation of propionaldehyde into α-methylpentenal, and then catalytic hydrogenation to obtain 2-methylpentenal. The catalytic hydrogenation reaction was carried out at 100°C and a pressure of about 1.4MPa, with a yield of 80%.
2. Preparation method:
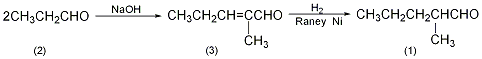
2-Methyl-pentene-2-aldehyde (3): In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, thermometer, and dropping funnel, add 20g of solid sodium hydroxide (0.5mol) and 650mL of water. Water bath cooling. Add 1000g (16.9mol) of 98% propionaldehyde dropwise at 20°C with stirring. After the addition is completed, the temperature is raised to 40°C and the reaction is maintained for 20 minutes. Cool to below 20°C, separate the organic layer, wash with a small amount of water, and distill under normal pressure. Collect the fraction between 125 and 140°C to obtain 1520g of 2-methyl-pentene-2-aldehyde (3), with a yield of 90%. 2-Methylpentanal (1): Add 1.5kg (15.3mol) of the above compound (3) and 100g of Ranney Ni catalyst into a high-pressure reaction kettle, replace the air with nitrogen, and then replace the nitrogen with hydrogen. Pass hydrogen at 100℃ and 1.3~1.5MPa pressure until the absorbed hydrogen reaches the theoretical amount or no more hydrogen is absorbed. After cooling, release the remaining liquid. Filter, the filter cake is Ranney Ni and can be reused. The filtrate was 2-methylpentanal (1), weighing 1220g, and the yield was 90%. [1]
Purpose
3. Usage: This product is an intermediate between the medicine metoplast and pesticides.