2-Nitroso-1-naphthol
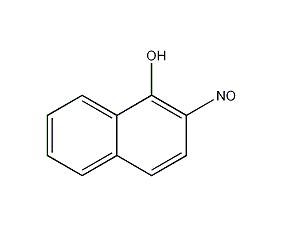
Structural formula
| Business number | 03NH |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H7NO2 |
| Molecular weight | 173.17 |
| label |
β-Nitroso-α-naphthol, 2-Nitroso-1-naphthyl alcohol, β-nitroso-α-naphthol, aromatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:132-53-6
MDL number:MFCD00003932
EINECS number:205-064-5
RTECS number:None
BRN number:1867919
PubChem number:QL4550000
Physical property data
1. Appearance: yellow needle crystal
2. Melting point (℃): 162-164
3. Solubility: soluble in methanol, ethanol, acetic acid, acetone, Slightly soluble in ether, benzene, chloroform and carbon disulfide, insoluble in water. The leaves are orange-yellow when soluble in organic solvents, dark red when soluble in concentrated sulfuric acid, and can evaporate with water vapor.
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity data:
Rat oral LD: >500mg/kg
Tumorigenicity data:
Rat oral TDLo: 31mg/ kg/1Y-I
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
5. Molecular property data:
1. Molar refractive index: 48.28
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 135.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 361.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 50.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 19.14
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 3
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 49.7
7. Number of heavy atoms: 13
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 195
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
It appears orange in organic solvents and orange-red in concentrated sulfuric acid. It forms yellow or orange-red insoluble in water with Co3+, ZrO2+, Fe2+ , etc. complex.
Storage method
Store in a cool, dry place and seal.
Synthesis method
Introduction to production method
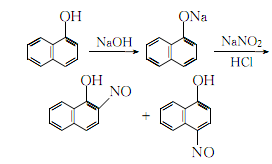
1. Obtained from nitrosation of 1-naphthol. 1. Nitrosation: Dissolve sodium hydroxide in water and add 1-naphthol while stirring. Filter, keep the filtrate at 0-5℃, add sodium nitrite aqueous solution,After finishing, slowly add acetic acid. Then adjust the pH with 1:4 dilute hydrochloric acid until the Congo red test paper turns blue. Use starch potassium iodide test paper to control the point, continue stirring for half an hour, filter out the nitrate, wash with water until it is no longer acidic, and dry. 2. After removing the isomer, nitrosation also generates 4-nitroso-1-naphthol, which can be removed by dissolving potassium hydroxide in alcohol, then slowly adding dry nitrate while stirring. At this time, the reaction temperature Keep at 60°C, complete the addition, and continue stirring for 10 minutes. Cool, filter out the crude product, add ethanol to soak, and filter. Finally refined to get the finished product.
2. Add α-naphthol to the sodium hydroxide aqueous solution while stirring, and filter out the insoluble matter. Control the temperature of the filtrate to 0~5°C, add sodium nitrite solution and acetic acid in sequence, and then adjust the H value with 1:4 dilute hydrochloric acid to make the Congo red test paper turn blue, and use starch potassium iodide test paper to control the end point of the reaction. After the reaction, continue stirring for half an hour, filter, then wash the nitrate crystals with water until they are no longer acidic, and dry. Slowly add the dried nitrate crystals to the ethanol solution of potassium hydroxide while stirring, keeping the temperature at 60°C. After that, continue stirring for 10 minutes, let it sit for natural cooling, filter the resulting crystals, soak them in ethanol, and then filter. Remove isomers  Dissolve the obtained crystals in hot In distilled water, add activated carbon for decolorization, add hydrochloric acid with stirring until the ph value of the filtrate is 5, wash the precipitate once with distilled water, and then recrystallize with ethanol to obtain the finished product.
Dissolve the obtained crystals in hot In distilled water, add activated carbon for decolorization, add hydrochloric acid with stirring until the ph value of the filtrate is 5, wash the precipitate once with distilled water, and then recrystallize with ethanol to obtain the finished product.
The reaction process formula is:

Purpose
1. Used to determine cobalt; zirconium; copper; iron and palladium. It can also be used in organic synthesis.
2.Used as a chromogen for photometric determination of cobalt, zirconium, etc. It is also used as an extraction agent for metal ions such as palladium. Also used as organic synthesis intermediates.