3,3-Dimethyl-2-butanone 3,3-Dimethyl-2-butanone


Structural formula
| Business number | 01KH |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H12O |
| Molecular weight | 100.16 |
| label |
Methyl tert-butyl ketone, 1,1,1-trimethylacetone, 3,3-Dimethylbutanone, Methyl tert-butyl ketone, 3,3-dimethyl-butan-2-one, pinacolone, 1,1-Dimethylethyl methyl ketone, 2,2-Dimethyl-3-butanon, α,α,α-Trimethylacetone, tert-Butyl methyl ketone, Pinacolone, Extracting agent |
Numbering system
CAS number:75-97-8
MDL number:MFCD00008846
EINECS number:200-920-4
RTECS number:EL7700000
BRN number:1209331
PubChem number:24887555
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless to light yellow liquid with mint smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -52.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 106.1[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.80 (25℃)[4]
5. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 4.2 (25℃)[5]
6. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -3483.7[6]
7. Critical temperature (℃): 290.9[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.32[8 ]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.2[9]
10. Flash point (℃): 23.89[10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 461[11]
12. Solubility: slightly soluble in Water, soluble in ethanol, ether and acetone. [12]
13. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.3943
14. Critical density (g·cm -3): 0.262
15. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 382
16. Critical compression factor: 0.276
17. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3785.36
18. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -290.67
19. The liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -328.54
20. Liquid phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -138.36
21. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 282.4
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat caliber LD50: 610mg/kg; mouse caliber LD50: 1625mg/kg; mouse inhalation LC50: 5700mg/m3: rabbit caliber LD50: 900mg/kg;
2. It is harmful and irritating to the body if inhaled, taken orally or absorbed through the skin. The LD50 for subcutaneous injection in guinea pigs is 700 mg/kg.
3. Acute toxicity[13]
LD50: 610mg/kg (mouse Oral)
LC50: 5700mg/m3 (mouse inhalation)
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[14] LC50: 87mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow, dynamic)
2. Biodegradability No information yet
3. Non-biodegradability[15] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 13d (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 29.84
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 124.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 271.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 22.2
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 11.83
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 17.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 76.7
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It is flammable and may cause fire and explosion when exposed to open flame, high heat or contact with oxidants.
2. Stability[16] Stable
3. Prohibited use Material[17] Strong oxidizing agent
4. Polymerization hazard[18] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[19] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Acetone method: Acetone is first reduced to pinacol, and then dehydrated and rearranged in acidic medium.
![]()
2. Isoamyl alcohol method Pentanol is dehydrated at high temperature to produce isopentene, which is obtained by reacting isopentene and formaldehyde in the presence of inorganic acid.
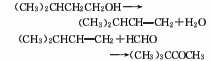
3. Tert-amyl alcohol method Pentanol is obtained by condensation and isomerization rearrangement with formaldehyde in hydrochloric acid. In addition, ponalone can also be obtained from 4,4,5-trimethyl-1,3-dioxane by boiling treatment with dilute inorganic acid or strong organic acid.

4. Preparation method:
p>
Into a 2L reaction bottle equipped with a dropping funnel and a distillation device, add 750g of 3mol/L sulfuric acid and 250g of hydrated pinacol (2). Heat and distill until the volume of the organic layer of the effluent no longer increases, which takes about 15 to 20 minutes. Separate the organic layer, add the aqueous layer to the distilling flask, add 60 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, drink 250 g of pinacol water, continue distillation, and repeat until a total of 1000 g of hydrated pinacol (4.42 mol) is added. The organic layers were combined and dried over anhydrous calcium chloride. Filter, fractionate, and collect fractions at 103 to 107°C to obtain 287 to 318 g of colorless liquid compound (1), with a yield of 65% to 72%. It turns light yellow after standing, and becomes colorless after re-distillation. [21]
Purpose
1. This product is used as solvent and extraction agent. It can also be used in organic synthesis. It reacts with hypochlorous acid to generate trimethylacetic acid; reacts with alkaline potassium permanganate aqueous solution and is oxidized into trimethylpyruvic acid; it easily undergoes condensation reactions with aldehydes, ketones, and acetic anhydride. Used for the production of pesticides and fungicides benzylchlorotriazole, triadimefon, triadimefon, diphenyltriadimefon, olefinazolidone, and octazolinone; Isoconazole, imazalil, etc. It is also used in the production of herbicides and pharmaceutical products.
2. Used as solvents and laboratory reagents. [20]