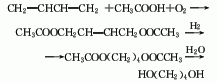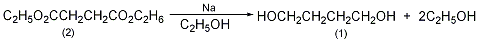

Structural formula
| Business number |
031N |
| Molecular formula |
C4H10O2 |
| Molecular weight |
90.12 |
| label |
butylene glycol,
1,4-Dihydroxybutane,
Butylene glycol,
1,4-Dihydroxybutane,
1,4-Butylene glycol,
Tetrasmethylene glycol,
softener,
water absorbent,
plasticizer,
lubricants,
humidifier,
softness,
adhesive,
Brightener for electroplating industry
|
Numbering system
CAS number:110-63-4
MDL number:MFCD00002968
EINECS number:203-786-5
RTECS number:EK0525000
BRN number:1633445
PubChem number:24854421
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless viscous liquid, needle-like crystals at low temperatures.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa): 228
3. Melting point (ºC): 19.9
4. Relative density (g/mL, 20 /4ºC): 1.017
5. Relative density (g/mL, 25/4ºC): 1.015
6. Refractive index (n25ºC): 1.4445
7. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 88.8
8. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 45.27
9. Flash point (ºC, opening): >121
10. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg): 576.1
11. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): 2518.8
12. Specific heat capacity (KJ/( kg·K), 20~75ºC, constant pressure): 2.41
13. Critical temperature (ºC): 446
14 Critical pressure (MPa): 6.2
15 Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K), 20ºC): 0.160
16. Solubility: Miscible with water, acetone and alcohol. Slightly soluble in ether, benzene, halogenated hydrocarbons, etc.
17. Refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.4462
18. Eccentricity factor: 1.189
19. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5:27.958
20. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 8.320×109
21. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol– 1): 57.000
22. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2576.5
23. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -426.7
24. Liquid phase standardu-2% Bi/magnesium silicate (the number is the mass fraction of metal in the catalyst) is the catalyst, the reaction temperature is 95°C, the acetylene partial pressure is 0.1MPa, and the pH value is 5-6. An inert gas is used as a diluent to reduce the partial pressure of acetylene thereby minimizing the risk of explosion. The conversion rate of butyne dry cup alcohol based on formaldehyde is 95%, and propargyl alcohol is recovered. The theoretical yield of butynediol is 95%. The hydrogenation process was improved to two-stage hydrogenation: 35% butynediol aqueous solution and copper acetate flow into the continuous stirred tank reactor, using Ranny Ni as the catalyst, operating at a temperature of 50-60°C and a hydrogen pressure of 1.4-2.0MPa. Crude BDO vapor containing partially hydrogenated and carbonyl compounds is produced. The crude BDO vapor is hydrogenated again in a fixed bed reactor filled with Ni-Cu-Mn/silica gel catalyst. The reaction temperature is 120-140°C and the hydrogen pressure is 13.8-20.7MPa. ISP Company’s research found that the silica gel carrier degraded itself under the conditions of the second stage of high-pressure hydrogenation reaction, causing reactor pressure pulsation. To this end, a new catalyst composed of 15%Ni-7%Cu-05%Mn/AI was developed. The catalyst has high activity under reaction conditions, is self-stable, and has a long life. The yield of 1,4-butanediol was 93.1% based on acetylene.

2. Maleic anhydride hydrogenation method. The production processes using butane as raw material include: Huntsman/Kvaerner method, BPAmcoc/Lurgi Geminox method and Sisas method. Among them, the Kvaerner process is as follows: using a vanadium-based catalyst on a fixed bed to oxidize n-butane into maleic anhydride (MA) in the gas phase, then convert maleic anhydride into the corresponding dimethyl maleic anhydride (DMM), and further gas phase hydrogenation /Hydrolysis gives BDO. MA and excess methanol undergo esterification reaction to generate DMM. Using acidic ion exchange resin as catalyst, at 70-80℃, MA conversion rate is 100%, DMM The yield is 99%. The DMM gas phase hydrogenation process uses copper as the initiator. At 170-190°C and 4-7MPa, the hydrogen/ester feed molar ratio of the reaction system is usually (250-350):1. The yield of crude BDO and GHF obtained by hydrogenation is greater than 99% based on DMM feed. The crude product is continuously distilled through multiple towers and refined into BDO, γ-butyrolactone, and tetrahydrofuran products. The methanol is recovered and recycled to the chemical preparation process. The total BDO yield based on MA is 98%-99%, and the main by-product is butanol (0.1%-0.2%).
3. The butadiene method involves the acetyl oxidation reaction of 1,3- butadiene with acetic acid and oxygen to generate 1 , 4-diacetoxy-2-butene is produced by hydrogenation and hydrolysis. The by-products THF and acetic acid are recycled.
4,1,4-dichlorobutene method 1,4-dichloro Butene is an intermediate product in the process of producing chloroprene from butadiene. It is used as raw material and is hydrolyzed and hydrogenated to obtain 1,4-butanediol.
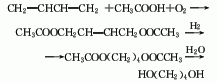
5. Preparation method:
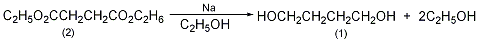
With a stirrer , two reflux condensers, and a 3L reaction bottle with a dropping funnel, add 60g (2.6mol) of fresh metallic sodium, and quickly add 35g (0.2mol) of diethyl succinate (2) and 700mL of absolute ethanol. The reaction proceeds vigorously and can be cooled in an ice-water bath if necessary. After the reaction is stable, heat the reaction (bath temperature can reach 130°C) to complete the reaction of metallic sodium (about 0.5 to 1 hour). Cool in an ice-water bath and filter out the precipitated sodium chloride. Add 300g anhydrous potassium carbonate to the filtrate to remove water and acid. Filter, and the filter cake is extracted twice with hot ethanol. Combine the filtrate and extract, evaporate the ethanol, and solid salt will precipitate. Add dry acetone, filter, and evaporate the acetone. The residue was distilled under reduced pressure, and the fraction at 133-135°C/2.4kPa was collected to obtain 13g of 1,4-butanediol (1), with a yield of 72%. [1]
Purpose
1. 1,4-Butanediol has many uses. More than half of it is used in the production of tetrahydrofuran in the United States and Western Europe, followed by the production of γ-butyrolactone and polybutylene terephthalate, the latter of which is a rapidly developing engineering plastic; 1,4-butanediol is used as an Chain agents and polyester raw materials are used to produce polyurethane elastomers and flexible polyurethane foams; esters made from 1,4-butanediol are good additives for cellulose, polyvinyl chloride, polyacrylates and polyesters. Plasticizer. 1,4-Butanediol has good hygroscopicity and flexibility, and can be used as gelatin softener and water absorbent, as well as a treatment agent for cellophane and other unused paper. It can also be used to prepare N-methylpyrrolidone, N-vinylpyrrolidone and other pyrrolidone derivatives. It is also used to prepare vitamin B6, pesticides, herbicides and solvents, lubricants, humidifiers, softness, Intermediates for brighteners, solvents, wetting agents and plasticizers in the adhesive and electroplating industries. Cross-linking agent and organic synthesis for manufacturing polyurethane elastomers. It can prepare N-methylpyrrolidone, N-vinylpyrrolidone and other pyrrolidone derivatives, and is also used to prepare vitamin B6, pesticides and herbicides. 2.Basic organic chemical raw materials with high added value are widely used in the field of fine chemicals. It can produce tetrahydrofuran (TH-F), γ-butyrolactone (GBL), N-methylpyrrolidone and N-ethylpyrrolidone, and is also used to produce high-functional polybutyl terephthalate (PBT) and Important raw materials for polyester engineering plastics, elastic fibers, polyester polyol and polytetramethylene ether glycol (PTMEG), polyurethane artificial leather, thermoplastic rubber, adhesives and pharmaceuticals. It can also be used as a chain extender for polyurethane to produce unsaturated polyester resin, etc.
Intermediates for brighteners, solvents, wetting agents and plasticizers. Cross-linking agent and organic synthesis for manufacturing polyurethane elastomers. It can prepare N-methylpyrrolidone, N-vinylpyrrolidone and other pyrrolidone derivatives, and is also used to prepare vitamin B6, pesticides and herbicides. 2.Basic organic chemical raw materials with high added value are widely used in the field of fine chemicals. It can produce tetrahydrofuran (TH-F), γ-butyrolactone (GBL), N-methylpyrrolidone and N-ethylpyrrolidone, and is also used to produce high-functional polybutyl terephthalate (PBT) and Important raw materials for polyester engineering plastics, elastic fibers, polyester polyol and polytetramethylene ether glycol (PTMEG), polyurethane artificial leather, thermoplastic rubber, adhesives and pharmaceuticals. It can also be used as a chain extender for polyurethane to produce unsaturated polyester resin, etc.