2,4′-Dibromoacetophenone 2,4′-Dibromoacetophenone
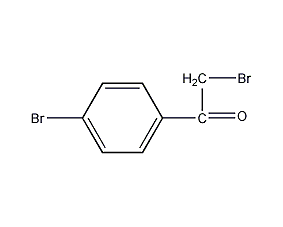

Structural formula
| Business number | 02GD |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H6Br2O |
| Molecular weight | 277.94 |
| label |
4-Bromobenzoylmethylchromium bromide, p-α-dibromoacetophenone, p-bromophenylacetyl bromide, p-bromoacetophenone, 2,4′-dibromoacetophenone, 2,4ˊ-Dibromoacetophenone, 2,4ˊ-Dibromoacetophenone, 4-bromophenylacetyl bromide, P-Bromophenacyl Bromide, Omega-Bromoacetophenone, 2-Bromo-1-(4-bromophenol)-ethanon, 4,alpha-Dibromoacetophenone, 4-Bromo(bromoacetyl)benzene, Protective agent |
Numbering system
CAS number:99-73-0
MDL number:MFCD00000200
EINECS number:202-783-6
RTECS number:AM6950000
BRN number:607604
PubChem number:24850825
Physical property data
1.Characteristics: off-white needle-like crystals. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 107~111[2]
3. Boiling point (℃) : 1415[3]
4. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.91[4]
5. Solubility : Insoluble in water, soluble in hot ethanol and ether. [5]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity:
Oral LD50 of mice: >2mg/kg;
Intravenous injection of mice LD50: 18mg/kg.
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 51.70
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 150.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 395.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 47.7
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 20.49
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 17.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 139
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[6] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[7] Strong oxidants, strong reducing agents, strong bases
3. Conditions to avoid contact[8] Heating
4. Polymerization hazard[9] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[10] Hydrogen bromide
Storage method
Storage Precautions[11] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from bromination of p-bromoacetophenone. Dissolve p-bromoacetophenone in glacial acetic acid and add bromine dropwise below 20°C.
2. In a 5-liter three-neck flask equipped with a stirrer, a separating funnel and a reflux condenser [connected to a hydrogen chloride absorption tank (Figure 5)], place 392 grams (2.5 mol) of olfactory benzene Dissolve in 1 liter of dry carbon disulfide solution (fireproof! Note 1), add 750 grams (5.6 moles) of anhydrous aluminum trichloride. Heat to slow reflux on a steam bath, then add dropwise 204 grams (2 mol) of acetyl alcohol (bp 136-139°C) for 1 hour. During the dripping process and within 1 hour after the dripping is completed, a slow reflux state should be maintained. The reaction is accompanied by the escape of a large amount of hydrogen oxide, and does not stop completely even after heating. The disulfide was evaporated directly from flask A on a steam bath. When it is slightly cold and the residue is still warm, slowly pour it into crushed ice mixed with hydrochloric acid while stirring. After the small amount of aluminum trichloride addition product remaining in the bottle is decomposed with ice-hydrochloric acid, combine the above of ice water solution, the total volume at this time is about 5 liters. Extract each 2 liters of mixture twice with 300 ml and 200 ml benzene (or ether). Combine the extracts and wash twice with water. After washing with 10% sodium hydroxide solution, wash twice with water until the water washing liquid is almost colorless, the two-phase solution can be quickly separated and all precipitates are separated with the water washing liquid. Add 30 grams of anhydrous calcium chloride to the benzene solution and dry for 1 hour, filter, and evaporate the solvent on a steam bath. The residue was distilled under reduced pressure on a short pine needle fractionating column. After the low boiling point substances are evaporated first, the temperature rises rapidly. If the hydrolysis step is done carefully and all aluminum salts are removed, the product should be a water-authentic fraction (boiling range 3°C), which will turn into white crystals when cooled.
3. Place 50 grams (0.25 mol) of p-bromoacetophenone and 100 ml of glacial acetic acid in a 500 ml flask, maintain the temperature below 20°C, and slowly drip while stirring Add 40 g (12.5 ml, 0.25 mol) bromine. When half the amount of O was dropped, needle-like crystals of ω-bromo-p-bromoacetophenone began to precipitate. After all the sniffing is completed (which takes 30 minutes), the cup is placed in an ice bath to cool down. Filter with suction, wash the crude product with 100 ml of 50% ethanol until colorless, and weigh 55-60 grams after drying. Recrystallize in 400 ml of 95% ethanol to obtain 40-50 g (69-72%) colorless needle-like crystals.
Purpose
1. Used in organic synthesis. [12]
2. Protection reagent for carboxylic acid and phenol, identification reagent for carboxyl and hydroxyl groups.