1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
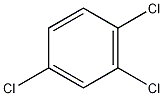
Structural formula
| Business number | 03CW |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H3Cl3 |
| Molecular weight | 181 |
| label |
Trichlorobenzene |
Numbering system
CAS number:120-82-1
MDL number:MFCD00000547
EINECS number:204-428-0
RTECS number:DC2100000
BRN number:956819
PubChem number:24862633
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid[1]
2. Melting point (℃): 17[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 213.5[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 1.45[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 6.26[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (38.4℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2798.7[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa ): 3.72[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 4.02[9]
10. Flash Point (℃): 105 (CC) [10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 571[11]
12. Explosion upper limit (%): 6.6[12]
13. Explosion lower limit (%): 2.5[13]
14. Solubility: insoluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol, miscible in ether, benzene, petroleum ether, carbon disulfide and most organic solvents. [14]
15. Viscosity (mPa·s, 55.4ºC): 1.5732
16. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol): 15.5
17. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 62.4
18. Refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.5717
19. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.5693
20. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5 :20.618
21.van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 1.233×1010
22. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 100.980
23. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 202.5
24. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol -1): 22.5
25. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 129.13
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity:
Rat oral LD50: 756mg/kg; rat subcutaneous LD50: 6139mg/kg; mouse oral LD50: 300mg/kg; mouse peritoneal cavity LD50 : 1223mg/kg;
2. Other multiple dose toxicity: Rat oral TDLO: 280mg/kg/14D-C; Rat oral TDLO: 7380mg/kg/13W-C;
3. Reproductive data: Rat oral TDLO: 1800mg/kg/25W-I; Rat (female) peritoneal TDLO: 750mg/kg/3D;
4. Mutagenic toxicity : Mouse micronucleus test: 210mg/kg/24H; 5. The toxicity is the same as that of dichlorobenzene, irritating the upper respiratory tract and mucous membranes. The olfactory threshold concentration is 0.01mg/L (water quality).
5. Acute toxicity [15]
LD50: 756mg/kg (rat oral); 6139mg/kg (rat transdermal); 6100mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
6. Irritation [16] Rabbit transdermal: 1950mg ( 13 weeks, intermittent), moderate stimulation.
7. Mutagenicity [17] Micronucleus test: mice were given the lowest toxic dose (TDLo) 210mg/kg intraperitoneally (24h)
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[18] LC50: 1.95mg/L (48h) (rainbow trout); 109mg/L (24h), 13mg/L (48h) ), 3.36mg/L (96h) (bluegill sunfish); 2.92mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow)
2. Biodegradability[19]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 672~4320
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 2688~17280
3. Non-biodegradability[20]
Photolysis maximum light absorption wavelength range (nm): 278~286
Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 128.4~1284
First-level hydrolysis half-life (h): 29784
4. Bioaccumulation [21 ] BCF: 420~1140 (carp, contact concentration 50μg/L, contact time 6 weeks); 120~1300 (carp, contact concentration 5μg/L, contact time 6 weeks)
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 40.93
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 125.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 314.8
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 39.9
5. Polarizability 16.22
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 94.3
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Dry and pure 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene is non-corrosive to metals. Under the action of heat and water, trace amounts of highly corrosive hydrogen chloride are released. Hydrolysis produces 2,5-dichlorophenol. Nitration produces 2,4,5-trichloronitrobenzene.
2. Stability[22] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[23] Strong oxidizing agent
4. Conditions to avoid contact[24] Heat
5.Polymerization hazard[25] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products[26] Hydrogen chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[27] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
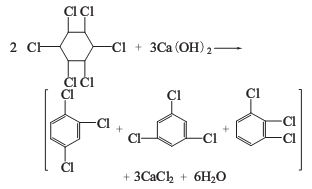
1. The nontoxic body of 666 dried by pyrolysis method is heated in a pyrolysis kettle to obtain trichlorobenzene, and a large amount of hydrogen chloride is produced as a by-product.
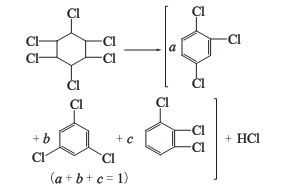
2. Alkaline hydrolysis method The six non-toxic substances are heated together with milk of lime to obtain trichlorobenzene, and a large amount of calcium chloride liquid is produced as a by-product.

Trichloride obtained by the above two methods Benzene is a mixture of three isomers: 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene; 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene; 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene. as the main component. Among the trichlorobenzene produced by the lime milk method, the content of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene is more than 75%, and 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene accounts for about 20%.
Purpose
1. Raw materials for medicines, dyes, and pesticides. It is also a raw material for widely used high-boiling point solvents and resistance fluids in transformers. It is used as a solvent for recrystallization of high melting point substances, coolant for electrical equipment, lubricating oil additives, degreasing agents, oil-soluble dye solvents, termite repellents, etc. It is also used as a raw material for the manufacture of 2,5-dichlorophenol. The industrial product is a mixture of various isomers (1,2,3-, 1,2,4-, 1,2,5-trichlorobenzene).
2. Used as solvents and synthesis of dyes, insulating liquids, pesticides, heat carriers, and in organic synthesis. [28]