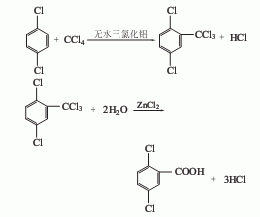
2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid 2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid
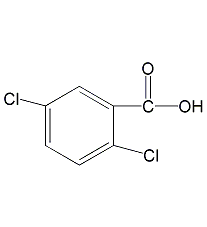
Structural formula
| Business number | 0146 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H4Cl2O2 |
| Molecular weight | 191 |
| label |
2,5-Dichlorobenzoic acid, Pesticides (Simplified Chinese); Aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:50-79-3
MDL number:MFCD00002416
EINECS number:200-065-7
RTECS number:DG6825000
BRN number:973353
PubChem number:24848693
Physical property data
1. Properties: White needle-like crystalline powder. Partially volatilized in steam.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 154.4°C (lit.)
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 301 °C (lit.)
6 . Boiling point (ºC, 5.2 kPa): Not determined
7. Refractive index: Not determined
8. Flash point (ºC): 300-302°C
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25 ºC ): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60 ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Soluble in ethanol and ether, soluble in hot water (<0.1 g/100 mL at 19 ºC).
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: mouse subcutaneous LD50: 1200mg/kg; mouse intraperitoneal LD50: 237mg/kg 2. Mutagenicity: mutation testing system – not other specifiedTEST systems: bacteria – Salmonella typhimurium: 1mg/L
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
None
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 37.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 161
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Uncertain chemical bond stereocenterAmount: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
None
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored in a dry place away from light. Storage and transportation according to regulations on toxic chemicals.
Synthesis method
1. Phosgene method: 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl chloride is obtained by reacting p-dichlorobenzene and phosgene, and then hydrolyzed.
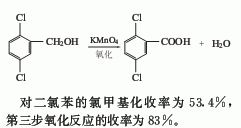
2. The chloromethylation method is obtained by reacting p-dichlorobenzene with paraformaldehyde and then oxidizing it with potassium permanganate. The yield of chloromethylation of p-dichlorobenzene was 53.4%, and the yield of the third step oxidation reaction was 83%
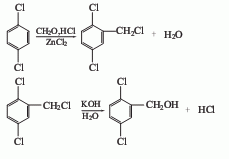
3. The trichlorobenzene method uses 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene as raw material to prepare 2,5-dichlorobenzonitrile and then undergoes alkaline hydrolysis.
4. Benzoyl chloride method is obtained by chlorination and hydrolysis of benzoyl chloride. The chlorination temperature of benzoyl chloride is controlled between 35-45°C. The main component of the chloride obtained is 2,5-dichlorobenzoyl chloride (content 65%). Then, in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, it is chlorinated at 40-45°C. Hydrolyzed at 50℃.
5. Dichlorobenzene carbon tetrachloride method.

Purpose
As an intermediate in organic synthesis. It is used to synthesize the herbicides legumin and dicaoping. This pesticide has less harmful effects and is not affected by rainy weather.