2,5-Dimethyl-2,5-hexandiol 2,5-Dimethyl-2,5-hexandiol
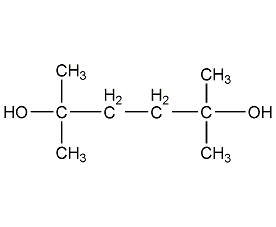
Structural formula
| Business number | 030F |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H18O2 |
| Molecular weight | 146 |
| label |
2,5-dimethyl-2,5-pentanediol, 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-hexanediol, 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-hexanediol, 1,1,4,4-Tetramethyl-1,4-butanediol, 2,5-Dimethylhexane-2,5-diol, Aliphatic alcohols, ethers and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:110-03-2
MDL number:MFCD00004473
EINECS number:203-731-5
RTECS number:None
BRN number:1361437
PubChem number:24848597
Physical property data
1. Properties: Prismatic crystals precipitate in ethyl acetate, and flake crystals precipitate in petroleum ether. White crystals.
2. Relative density (g/mL, 20/20℃): 0.898
3. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 0.898
4. Melting point (ºC): 92
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 214
6. Crystalline phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -5038.8
7. Crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -681.7
8. Flash point (ºC): 126
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16 . The logarithmic value of the oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. The upper limit of explosion (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. The lower limit of explosion (%) ,V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Soluble in water, acetone, ethanol, benzene, chloroform, insoluble in carbon tetrachloride and kerosene.
Toxicological data
None yet
Ecological data
This substance may be harmful to the environment and special attention should be paid to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 42.11
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 155.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 374.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 33.3
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 16.69
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.8
2. Hydrogen bondingNumber of polymers: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Tautomers Number: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 40.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 91.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain Number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determined number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15 .Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
No contact with strong oxidizing agents.
The toxicity is unknown. But there are also reports that it is not toxic.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 30℃. Keep container tightly sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Packaged in iron drums lined with plastic bags. Protect from sun, heat and moisture during storage. Store and transport according to general chemical regulations.
Synthesis method
1. Acetylene-acetone method: Acetylene and acetone are condensed with potassium hydroxide in a benzene solvent, then acidified with hydrochloric acid, and then hydrogenated.
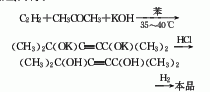
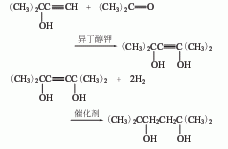
2. Methylbutynol -Acetone condensation method.
3. Most of the industrial production of 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-hexanediol uses acetylene and acetone as raw materials. In the past, the atmospheric pressure alkynylation method was widely used. The process route is: Three steps: alkynylation, hydrolysis and hydrogenation at normal pressure. Acetylene and acetone undergo an alkynylation reaction with excess potassium hydroxide in a solvent under normal pressure to generate potassium 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne-2,5-diolate, which is then hydrolyzed under acidic conditions. 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne-2,5-diol is generated, and finally the product is obtained by catalytic hydrogenation using Raney nickel as a catalyst under a pressure of 2 to 2.5 MPa.
Atmospheric pressure alkynylation technology is relatively mature, but for the gas-liquid phase alkynylation reaction, the production efficiency of normal pressure operation is low from a kinetic point of view, and it can only be carried out intermittently. In addition, potassium hydroxide is consumed. The quantity is large, it is inconvenient to recycle, the equipment is seriously corroded, and the operation is troublesome.
The pressurized alkynylation method developed by the Southwest Research Institute of Chemical Industry in my country is used to prepare 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-hexanediol. The process consists of three steps: pressurized alkynylation, condensation and hydrogenation. Acetylene is React with acetone in an autoclave at a pressure of 18 to 20 kgf/cm2 (1kgf/cm2=98.0665kPa) and a temperature of 35 to 40°C to form 2-methyl base-3-butyn-2-ol, and then condensed with acetone at 30~50℃ to form 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyn-2,5-diol, and finally at 10kgf/cm 2 Pressure, using Raney nickel as the catalyst, catalytic hydrogenation at 30 to 80°C to obtain the product.
The pressure alkynylation method can produce continuously and has high production efficiency. The consumption of potassium hydroxide is only 1/6 to 1/4 of that of the normal pressure alkynylation method, and the amount of alcohol hydrolyzed by alcohol is also reduced accordingly. , equipment corrosion is reduced, and Yangzhou Chemical Plant adopts this method for production.
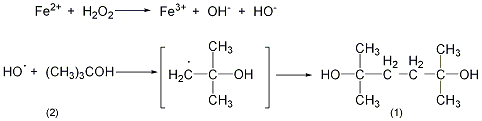
4. Preparation method:
p>

In 5L container equipped with stirrer and thermometer In a four-neck reaction bottle, add 1500mL of water, 28mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, and 900mL of tert-butanol (2) (702g, 9.47mol). After replacing the air with nitrogen, cool it to 10°C in an ice bath. Add two solutions simultaneously while stirring: 86mL. (1mol) 35% hydrogen peroxide (5% ~ 50%): a solution of 278g (1.0mol) ferrous sulfate pentahydrate, 570mL water, and 55.5mL (1.0mol) concentrated sulfuric acid. Control the temperature below 20°C and complete the addition in 20 minutes. After the addition is completed, add 50 mL (1.0 mol) of 52% sodium hydroxide solution dropwise with stirring. Then add 450g of anhydrous sodium sulfate to keep the reaction system below 20°C. Separate the organic layer and neutralize it to pH 7 with 52% sodium hydroxide solution. The aqueous layer was extracted with 400 mL of tert-butanol, and neutralized to pH 7 with 52% sodium hydroxide. Combine the resulting aqueous phases and extract with 400 mL of tert-butyl alcohol. The four organic layers were combined and concentrated under reduced pressure until there was no tert-butyl alcohol (70°C/665Pa). The residue was extracted with 2L ether and decolorized with activated carbon. Recover diethyl ether to obtain light yellow crystal ①(1) 30-45g, with a yield of 41%-62% (calculated as hydrogen peroxide). The product was boiled with 30 mL of diethyl ether and 70 mL of cyclohexane, and filtered to obtain 29 to 34 g of white crystals, with a yield of 40% to 46%. It can be further purified by recrystallization, ethyl acetate 1:4, cyclohexane 1:20, water 1:2. Note: ① Using similar synthesis methods, the following compounds can be synthesized: tetramethyladipic acid is synthesized from pivalic acid, tetramethyltetramethyltetramethyldiamine is synthesized from tert-butylamine, and tetramethylhexane is synthesized from pivalonitrile. dinitrile. [1]
Purpose
Used as solvent and organic synthesis intermediate. Mainly used in the production of pesticide pyrethrins, spices, organic peroxides, artificial musk, polyethylene plastic cross-linking agents and polyether rubber.