Acetone cyanohydrin Acetone cyanohydrin
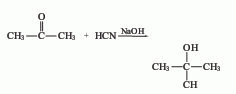
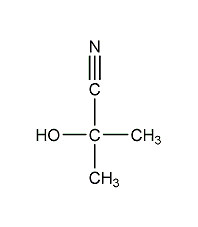
Structural formula
| Business number | 01KA |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H7NO |
| Molecular weight | 85.10 |
| label |
1-acetone cyanohydrin, 1-Hydroxyisobutyrontrile, 2-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile, pesticides, Metal separation and refining agent, Multifunctional solvents, synthetic raw materials, Intermediates |
Numbering system
CAS number:75-86-5
MDL number:MFCD00004455
EINECS number:200-909-4
RTECS number:OD9275000
BRN number:605391
PubChem number:24844886
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless to light yellow liquid.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 0.932
3. Melting point (ºC): -19
4. Boiling point (ºC , normal pressure): 82 (3066pa)
5. Refractive index (15ºC): 1.3980
6. Flash point (ºC): 63
7. Flash point (ºC): 687.78
8. Vapor pressure (kPa, 82ºC): 3.07
9. Solubility: miscible with water, alcohol, ether and other organic solvents dissolve. Insoluble in petroleum ether and carbon disulfide.
Toxicological data
This product is highly toxic, with an oral LD50 of 15mg/kg in mice. Guinea pig transdermal LD50 is 140mg/kg. Rabbits coated with 100 mg/kg skin died within 5 to 180 minutes. A rabbit will die immediately if one drop is put into its eye. This product can be absorbed through the respiratory tract, skin and digestive tract and cause poisoning. Acute poisoning has an incubation period, the length of which is related to the amount of poison. Symptoms generally appear 4 to 5 minutes after exposure. Early symptoms include weakness, dizziness, headache, chest tightness, palpitations, nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite. This was followed by difficulty breathing, loss of consciousness, and convulsions. Finally died due to respiratory arrest.
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 21.99
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 85.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 211.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 37.3
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.71
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.1
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
p>
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 44
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9.�Impurity: 87
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determined number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain atomic configuration Number of centers: 0
13. Determined number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Covalent Number of key units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It easily decomposes when exposed to alkali or heat, releasing highly toxic hydrogen cyanide. A small amount of sulfuric acid is often added to the finished product to make it acidic or neutral to reduce decomposition. It should be protected from heat or sunlight during storage or transportation to avoid poisoning or explosion accidents due to the production of large amounts of hydrogen cyanide.
Chemical properties: Acetone cyanide is an intermediate for the synthesis of methacrylic acid from acetone. It is prone to alkaline hydrolysis to generate acetone and hydrogen cyanide. After acetylation, the hydroxyl group in acetone cyanide is pyrolyzed to form methacrylonitrile.
2.It is very toxic to the respiratory and digestive systems, and will also produce moderate toxicity after skin absorption. Mice will die within 90 seconds when exposed to steam. The production workshop should be well ventilated, operators should wear special protective clothing, and no part of the body should be exposed. Those who are poisoned should seek medical treatment immediately. Rat oral LD50170mg/kg.
3. It can be decomposed into hydrocyanic acid and acetone and is not suitable for distillation.
4. Exist in smoke.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool and dry seal. It should be protected from heat or sunlight during storage or transportation.
2. The production and use of this product are always in the same place, and no transportation is required. Store and transport according to regulations on toxic chemicals.
Synthesis method
The reaction between sodium cyanide and concentrated sulfuric acid produces hydrocyanic acid. After purification by distillation, hydrocyanic acid reacts with acetone to form acetone cyanohydrin: the raw material hydrocyanic acid can also use the by-product of acrylonitrile. Laboratory synthesis or reagent production is the same as the above process route. The operation method is as follows: In a 5L three-necked flask, add a solution composed of 500g (9.7mol) powdered sodium cyanide and 1.2L water and 900ml (713g, 12.3mol )acetone. Place the flask in an ice bath and stir vigorously. When the temperature drops to 15°C, slowly add 2.1L (8.5mol) 40% sulfuric acid, complete the addition within 3 hours and maintain 10-20°C. After adding the acid, continue stirring for 15 minutes. Let sit to allow the salt to settle. Pour out the generated acetone cyanohydrin by decantation to separate it from the water layer. The sodium cyanide sulfate in the aqueous layer was filtered off and washed with acetone. The filtrate and washings were combined and extracted with diethyl ether. Combine the extract with the previously separated acetone cyanohydrin. Dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Evaporate off the ether and acetone on a water bath. The residue was distilled under reduced pressure at 2.0-2.67kPa, and the 78-82°C fraction was collected. The obtained product is 640-650g, and the yield is 77-78%. Product specifications: As an intermediate in the production of organic glass, it is a brown liquid with a content of ≥93%. Raw material consumption quota: sodium cyanide (>93%) 557kg/t, acetone (98%) 650kg/t, sulfuric acid (93%) 704kg/t.
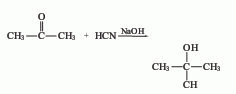
Refining method: anhydrous sodium sulfate After drying, distill under reduced pressure, but be careful about decomposition.
Purpose
1. Important organic synthesis intermediates, used in the synthesis of methacrylic acid, methacrylate, methacrylonitrile, methyl methacrylate, ethyl 2-methylisobutyrate, and azobisisobutyronitrile. , pesticides and metal separation and refining agents.
2. Pesticide preparation. Organic Synthesis.