Acrylic acid Acrylic acid
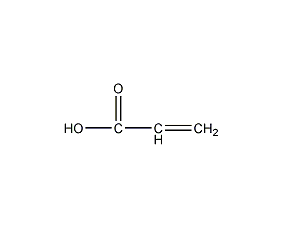

Structural formula
| Business number | 01PB |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H4O2 |
| Molecular weight | 72.06 |
| label |
2-Acrylic acid, Polymer grade acrylic, benzoic acid, vinylformic acid, Propenoic acid, Acrylic acid (HPAA), Vinyl formic acid, Ethylenecarboxylic acid, 2-Propenoic acid, Acrylsaeure, acid solvents, aliphatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:79-10-7
MDL number:MFCD00004367
EINECS number:201-177-9
RTECS number:AS4375000
BRN number:635743
PubChem number:24845189
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with pungent odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 13[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 141 [3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.05[4]
5. Relative vapor density (Air=1): 2.45[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 1.33 (39.9℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1366.9[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 5.66[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.36[9]
10. Flash point (℃): 54 (CC); 54.5 (OC)[10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 360[11]
12. Explosion upper limit (%): 8.0[12]
13. Explosion lower limit (%): 2.4[13]
14. Solubility: miscible with water, miscible with ethanol and ether. [14]
15. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 1.149
16. Heat of vaporization (KJ/mol): 45.6
17. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol, 13ºC): 11.1
18. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.050
19. Relative density (25 ℃, 4℃): 1.044
20. Refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.422
21. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 26.229
22. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 6.000×109
23. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1) : 39.930
24. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -1368.43
25. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (Enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -383.76
26. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 226.4
27. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 144.2
28. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -1428.7
29. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -323.5
30. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 307.73
31. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -271.0
There are trace amounts of acrolein, acetic acid, valeric acid, formic acid and other aldehyde impurities. Aldehydes are by-products of propylene oxidation or generated by the oxidation of impurities contained in propylene raw materials, such as acetaldehyde, formaldehyde, benzaldehyde, furfural, acrolein, etc. The reaction gas containing these by-products is cooled and extracted and distilled. , remaining in acrylic products. Acrylic products refined by conventional methods still contain about (50-500) ×10-6 aldehyde substances. In order to meet the needs of high-purity acrylic acid, Beijing Dongfang Chemical Plant used the plant’s polymer-grade acrylic acid as raw material to develop a method for preparing high-purity acrylic acid, so that the total aldehyde content is less than 5×10-6, reaching or exceeding relevant foreign literature reports Data requirements (foreign countries are less than 10×10-6). The experimental method is: add a certain amount of polymer grade acrylic acid to the flask, add the reagent DL, and then process it in the range of 10 to 80°C under normal pressure, and then enter the packed tower for distillation. The temperature in the tower still is 60 to 80°C. , the temperature at the top of the tower is 50~70℃, the vacuum is 93.33~99.99KPa, and the method of adding polymerization inhibitor and gas phase polymerization inhibitor is used to prevent acrylic acid from being distilled during rectification polymerization in the process. The distillate collected by this method is high-purity acrylic acid.
② Fluidized bed method. The production method is that propylene, air, and water pass through the first ebullating bed reactor to generate acrolein, then enter the second ebullating bed reactor to generate acrylic acid, and then undergo spraying, cooling, extractive distillation, and then remove the acetic acid in the pressure reduction tower. Get acrylic. The ratio of the oxidation mixture is propylene: air: water = 1:12:8 (molar ratio). The temperature of the first ebullated bed reactor is 370°C, and the contact time is 2s; the temperature of the second ebullated bed reactor is 260°C, and the contact time is 2.25s. The propylene conversion rate is 75% to 80%, the total yield is 40%, the acrylic acid content is 97%, and the average content is 93%. In China, a seven-component (molybdenum-vanadium-phosphorus-iron-cobalt-nickel-potassium) catalyst is used in the first reactor to oxidize propylene to produce acrolein; a three-component component (molybdenum- Vanadium-tungsten) catalyst, acrolein oxidation to acrylic acid, when propylene: air: water = 1:10:6, contact time 5.5s, linear speed 0.6m/s reaction temperature: one stage is 370-390 ℃, the second stage is At 270 ~ 300°C, based on the feed propylene, the first-stage propylene conversion rate is 78.7% ~ 87%, the acrolein yield is 51.9% ~ 57.2%, and the second-stage propylene conversion rate The rate is 79.3% to 89.4%, the acrylic acid yield is 48.3% to 49.8%, and the acrylic acid yield is 55 to 60kg/(m3 catalyst·h).
Purpose
1. Acrylic acid and its series of products, mainly its esters, have developed rapidly in recent years. Such as ethylene, propylene, vinyl chloride, acrylonitrile, etc., have developed into important raw materials for the polymer chemical industry. As monomers of polymer compounds, the world’s total output of acrylic acid and its esters has exceeded one million tons, while the output of polymers and copolymers (mainly emulsion resins) made from them has reached nearly 5 million tons. These resins are used in coatings, plastics, textiles, leather, paper, building materials, packaging materials and many other sectors. Acrylic acid and its esters can be used for organic synthesis and polymer synthesis, and most of them are used in the latter, and are more often copolymerized with other monomers, such as vinyl acetate, styrene, methyl methacrylate, etc. Synthetic resins, functional polymer materials and various additives with various properties are produced.
2. Main application areas: (1) Warp sizing materials prepared from acrylic acid, methyl acrylate, ethyl acrylate, acrylonitrile, ammonium polyacrylate and other raw materials are more effective than polyvinyl alcohol. The capacity of sizing material is desizing, saving starch.
(2) The adhesive uses copolymer latex such as acrylic acid, methyl acrylate, ethyl acrylate, and 2-ethylhexyl acrylate. It can be used as an adhesive for electrostatic flocking and hair transplantation. Its fastness and feel good.
(3) Water thickener is a high molecular weight powder made from acrylic acid and ethyl acrylate copolymer. It can be used as a thickening agent in oil fields. Each ton of product can increase the production of crude oil by 500t, and has a good effect on oil recovery from old wells.
(4) Coated paper coating agent uses acrylic acid, butyl acrylate, 2-ethylhexyl acrylate, styrene and other quaternary copolymer latex as coated paper coating, which maintains color without yellowing and improves printing performance. Good, non-stick roller, better than styrene-butadiene latex and can save desiccant.
(5) Polyacrylate Acrylic acid can be used to produce various polyacrylate products (such as ammonium salt, sodium salt, potassium salt, aluminum salt, nickel salt, etc.). Used as coagulant, water treatment agent, dispersant, thickener, food preservative, acid and alkali resistant desiccant, softener and other polymer additives.
3. Important organic synthetic raw materials and synthetic resin monomers are vinyl monomers that polymerize very quickly. Most of them are used to make acrylates such as methyl acrylate, ethyl acrylate, butyl acrylate, and hydroxyethyl acrylate. Acrylic acid and acrylic esters can be homopolymerized or copolymerized, and can also be copolymerized with monomers such as acrylonitrile, styrene, butadiene, vinyl chloride, and maleic anhydride. Its polymers are used in industrial sectors such as synthetic resins, adhesives, synthetic rubber, synthetic fibers, super absorbent resins, pharmaceuticals, leather, textiles, chemical fibers, building materials, water treatment, oil exploration, and coatings. Acrylic acid is one of the important raw materials for water-soluble polymers. It can be grafted and copolymerized with starch to produce super water-absorbing agents.
4. Preparation of acrylic resin, rubber synthesis, coating preparation, pharmaceutical industry.
5. Used in resin manufacturing. [28]
��Pharmaceutical industry.
5. Used in resin manufacturing. [28]