Bromoacetic Acid Bromoacetic Acid
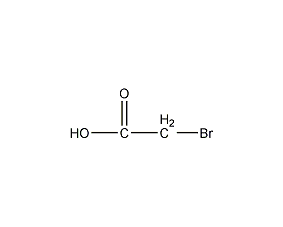
Structural formula
| Business number | 01P9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H3BrO2 |
| Molecular weight | 138 |
| label |
Monobromoacetic acid, Pesticide intermediates; aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:79-08-3
MDL number:MFCD00002678
EINECS number:201-175-8
RTECS number:AF5950000
BRN number:506167
PubChem number:24855703
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless crystal, easy to deliquesce. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 49~51[2]
3. Boiling point (℃) :208[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.934[4]
5. Saturation Vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (54.7℃)[5]
6. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.41[6]
7. Solubility: Easily soluble in water, ethanol, ether, and soluble in acetone and benzene. [7]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[8] LD50: 100mg/kg (oral mouse)
2. Irritation No data yet
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity [9] Pigs, fed 10~54mg/(kg·d) , died of poisoning on 28 to 105 days, with obvious gastroenteritis, jaundice and muscle weakness.
4. Sensitization[10] Skin sensitization
5. Mutagenicity[11] DNA damage: mouse leukocytes 100μmol/L. DNA damage: hamster ovary 0.017mmol/L (4h)
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability No information available
4. Other harmful effects[12] This substance is harmful to the environment and should be treated with special Pay attention to water pollution.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 20.61
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 69.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 185.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 51.3
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3):8.17
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.4
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 37.3
6. Number of heavy atoms: 5
7. Surface charge: 0
8. Complexity: 42.9
9. Number of isotope atoms: 0
10. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters : 0
11. The number of uncertain atomic stereocenters: 0
12. The number of determined chemical bond stereocenters: 0
13. Uncertain chemical bond stereocenters Number of structural centers: 0
14. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[13] Stable
2. Incompatible materials [14] Strong oxidants, strong bases
3. Conditions to avoid contact [15] Light, heat
4. Polymerization hazard[16] No polymerization
5. Decomposition Product[17] Hydrogen bromide
Storage method
Storage Precautions[18] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. It is prepared by using acetic acid as raw material and adding bromine dropwise in the presence of pyridine for reaction.
![]()
2. From chloroacetic acid and hydrogen Obtained from the reaction of bromic acid.
![]()
3. From glycolic acid and hydrogen Obtained from the reaction of bromic acid.
![]()
4. Preparation method:
p>
Add glacial acetic acid (2) 131g ( 2.2mol), acetic anhydride 27g (0.26mol), pyridine 0.25mL. Heat the mixture to boiling, first add 1 mL of bromine to start the reaction, wait until the color of bromine disappears, then slowly add bromine (140 g in total, 0.875 mol) dropwise, and finish the addition in about 2 hours. After the addition is complete, continue the reflux reaction until the color of bromine disappears. Cool and slowly add 10 mL of water to decompose the anhydride. Acetic acid and water are distilled off, and the residue is crude bromoacetic acid. Solidify after cooling, distill the crude product, and collect the fractions at 202-204°C, or collect the fractions at 117-118°C/2.0kpa by distillation under reduced pressure to obtain 100g of bromoacetic acid (1), mp50°C, yield 83%. [20]
Purpose
Used in organic synthesis. [19]