Caffeine Caffeine
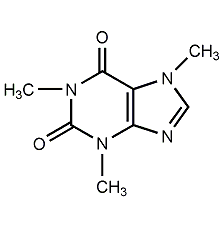

Structural formula
| Business number | 0196 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H10N4O2 |
| Molecular weight | 194.19 |
| label |
1,3,7-Trimethylxanthine, 1,3,7-Trimethylxanthine, Stimulants, bitters and flavors |
Numbering system
CAS number:58-08-2
MDL number:MFCD00005758
EINECS number:200-362-1
RTECS number:EV6475000
BRN number:17705
PubChem number:24277682
Physical property data
1. Properties: It usually exists in the form of no crystal water and one crystal water, and is white powder or white needle crystal. Odorless, bitter taste. 2. Density (g/mL, 18/4℃): 1.233. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 238℃, sublimation at 178℃. Under the pressure of 133 Pa, it sublimates very quickly at 160-165℃.
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition Combustion temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Logarithmic value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Each gram of caffeine is soluble in 46 ml of water, 5.5 ml of hot water (80°C), 1.5 ml Boiling water, 66 ml ethanol, 22 ml hot ethanol (60°C), 50 ml acetone, 5.5 ml chloroform, 530 ml diethyl ether, 100 ml benzene, or 22 ml boiling benzene. Very soluble in pyrrole and tetrahydrofuran containing 4% water. Soluble in ethyl acetate, slightly soluble in petroleum ether. The solubility of the salts of this product in water increases in order of benzoate, cinnamate, citrate, and salicylic acid; caffeine hydrochloride, sulfate, and phosphate are all easily soluble in water or alcohol, and Decomposes into free base and acid.
Toxicological data
None yet
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 50.38
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 133.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 364.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 55.7
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 19.97
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.1
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 58.4
7. Number of heavy atoms: 14
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 293
10. Isotopic atoms Quantity: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the chemical bond positions Number of stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
It has the function of stimulating the central nervous system and is addictive.
Storage method
Sealed packaging in non-toxic plastic bags or glass bottles. Store in a cool and dry place.
Synthesis method
1. Urea method: chloroacetic acid is neutralized, cyanated, and acidified to obtain cyanoacetic acid, which is then condensed with urea to obtain cyanoacetyl urea, which is then cyclized, acidified, nitrosated, reduced, acylated, and methylated to obtain cyanoacetic acid. caffeine.
2. The dimethylurea method condenses urea and monomethylamine to form dimethylurea, and then condenses with cyanoacetic acid to form 1,3-dimethylacetylurea, and then undergoes cyclization; nitrosation; reduction; Acylation; cyclization; methylation to obtain caffeine. The dimethylurea method has high yield, low cost, low consumption, short cycle, low equipment requirements, simple operation, easy control, and is suitable for industrial production. Additionally, when producing low-caffeine coffee, caffeine is obtained as a by-product. In addition to the methods of extraction from natural substances and the above-mentioned fully synthetic methods, there are also semi-synthetic methods. Theobromine is extracted from human cocoa and then methylated to obtain caffeine, which is an earlier semi-synthetic method. The preparation of caffeine from bird guano or uric acid also belongs to this type of synthesis.
3.Neutralization, cyanation, and acidification of chloroacetic acid yield cyanoacetic acid, which is then condensed with urea to yield cyanoacetylurea, which is then acidified, nitrosated, and reduced , acylation, and methylation to obtain caffeine. It can also be extracted from tea leaves, coffee beans, and cocoa.
4.The main preparation method is natural product extraction. Put 100g tea leaves into the filter paper cylinder of the Soxhlet extractor, add 670ml of 95% ethanol, add another 330ml of ethanol into the flask, heat and reflux in a water bath to extract, until the extract color until it becomes shallower (2.5~3h). Then, decolorize the extract with activated carbon. After decolorization, filter it while hot to obtain a brown liquid. Distillate to recover ethanol (about 420ml). Pour out the remaining liquid while hot, add 45g of quicklime powder, stir into a slurry, and evaporate on a steam bath. Caffeine can be obtained by drying it into powder and then separating it by sublimation.
Purpose
1. Mainly used as stimulants, bitters and spices. Can be used in cola-type drinks and coffee-containing drinks. The maximum allowable dosage is 200mg/kg.
2.It has the effect of stimulating the central nervous system such as refreshing and refreshing. Our country stipulates that it can be used in cola-type beverages, and the maximum usage amount is 0.15g/kg.