Citronellol Citronellol
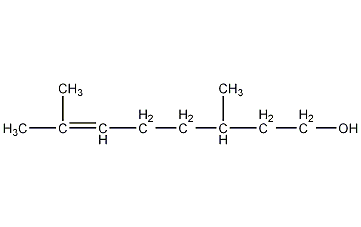

Structural formula
| Business number | 02SW |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H20O |
| Molecular weight | 156.27 |
| label |
3,7-Dimethyl-6-octenol, 3,7-dimethyl-6-octen-1-ol, 2,6-Dimethyl-2-octen-8-ol, β-Citronellol, artificial flavors, alcohol solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:106-22-9
MDL number:MFCD00002935
EINECS number:203-375-0
RTECS number:RV3400000
BRN number:1721507
PubChem number:24893050
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless oily liquid with a special aroma like fresh roses and a bitter taste.
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): 0.857
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 5.4
4. Melting point (ºC): 77-83
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 224.5
6. Boiling point (ºC, mmHg):
7. Refractive index (n20D): 1.456
8. Flash point (ºC): 79
9. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 0.8549
10. Refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.4543
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, 25ºC): ~0.02
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (octanol/ Log value of the distribution coefficient (water): Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Soluble in ethanol and most non-volatile oils and propylene glycol, insoluble in glycerol and poorly soluble in water.
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation: Standard Dresser test: Male skin contact, 16mg/48HREACTION SEVERITY, moderate reaction; Standard Dresser test: Rabbit skin contact, 100mg/24HREACTION SEVERITY, strong reaction; Standard Dresser test: Guinea pig skin contact, 100mg/24HREACTION SEVERITY, strong reaction; 2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 3450mg/kg; mouse subcutaneous LD50: 880mg/kg; mouse muscle LD50: 4mg/kg; Rabbit skin contact LD50: 2650mg/kg
Ecological data
It is extremely harmful to water and toxic to fish. Do not let the product enter the water body.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 49.77
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 184.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 427.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 28.5
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 19.73
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 3.2
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 5
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 20.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 112
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with oxidants. Colorless oily liquid with a special aroma like fresh roses and a bitter taste. There are three natural products: d-, dl- and l-. L-citronellol is rhodinol (see this article). Citronellol, as it is generally called, refers to d-citronellol. Soluble in ethanol and most non-volatile oils and propylene glycol, insoluble in glycerol and poorly soluble in water. Natural citronellol (d-type) exists in more than 70 kinds of essential oils such as citronella oil and geranium oil.
2. Found in burley tobacco leaves.
3. It naturally exists in more than 70 kinds of plants, including East African geranium oil, Guawa citronella oil, rose oil, etc.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. (1) D- and racemic citronellol are produced from the citronellal part of essential oils. D-citronellal, which is distilled from Java vanilla oil, is converted into d-citronellol by contact hydrogenation with Raney nickel catalyst. Similarly, racemic citronellol is obtained from the racemic citronellal part in lemon eucalyptus oil. (2) Manufactured from d- or racemic geraniol in essential oils. Geranium obtained from Javanese citronella oil is obtained by catalytic hydrogenation and then fractional distillation. Selecting Raney cobalt as a catalyst can hydrogenate the 2-position double bond. (3) Obtained by partial hydrogenation of a synthetic mixture of geraniol and nerolidol; or produced by reacting isopropyl alcohol with barium-activated copper subargenate under pressure at 180°C. The yield of this method is 90%. (4) L-citronellol is produced from optically active pinene. Hydrogenate α- or β-pinene to obtain (-)-cis-pinene, which is transformed by thermal cracking into (+)-3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadiene, which can be combined with triisobutylaluminum or dimethyl Isobutylaluminum hydride is used, and then the generated aluminum alkoxide is oxidized and hydrolyzed to obtain citronellol with a purity of 97%.
2. Tobacco: BU, 14:.
Purpose
1. It has a more elegant rose aroma than geraniol. It is an indispensable raw material for formulating various rose-based floral flavors and can be used in a variety of cosmetic flavors.
2. Easy to esterify with organic acids.