Dibutyltin Maleate Dibutyltin Maleate

Structural formula
| Business number | 01MM |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C12H20O4Sn |
| Molecular weight | 346.99 |
| label |
dibutyltin maleate, dibutyltin maleate, dibutyltin maleate, dibutyltin butenedioate, Anhydrous dibutyltin malate, 2,2-Dibutyl-1,3,2-dioxastantin-4,7-dione, dibutyltin maleate, 2,2-dibutyl-1,2,3-dioxastannepin-4,7-dione, DBTM, Heat stabilizers |
Numbering system
CAS number:78-04-6
MDL number:MFCD00014120
EINECS number:201-077-5
RTECS number:JH4735000
BRN number:None
PubChem number:24867599
Physical property data
1. Appearance: White amorphous powder
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): Uncertain
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL , air=1): Uncertain
4. Melting point (ºC): 108-113℃
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Uncertain
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Uncertain
7. Refractive index: Uncertain
8. Flash point (ºC): Uncertain
9. Specific optical rotation (º): Uncertain
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Uncertain
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC) : Uncertain
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Uncertain
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Uncertain
14 . Critical temperature (ºC): Uncertain
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Uncertain
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Uncertain
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
19 . Solubility: Slightly soluble in benzene and toluene, insoluble in water.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity
Rat inhalation LC50: 313 mg/m3/4H
Mouse LD50: 470 mg/kg;
2 , Reproductive toxicity:
Rat caliber LD50: 28 mg/kgSEX/DURATION Mouse half-lethal dose (intravenous): 56mg/kg
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
None yet
Compute chemical data
1. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
2. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
3. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 6
4. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 52.6
5. Number of heavy atoms: 17
6. Surface charge: 0
7. Complexity : 282
8. The number of isotope atoms: 0
9. The number of determined atomic stereocenters: 0
10. The number of uncertain atomic stereocenters: 0
11. Determined number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
12. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
13. Number of covalent bond units :1
Properties and stability
It is irritating, toxic and tear-inducing.
Storage method
This product should be kept sealed. Packed in cardboard drums, the product is stored in a ventilated and dry place.
Synthesis method
(1) Synthesis of dibutyltin oxide. Put red phosphorus and butanol into the reaction kettle at room temperature, then add iodine in batches and stir while adding. As the reaction proceeds, the temperature gradually increases. When the temperature reaches 127°C When left or right, stop reacting. Add water to wash and let stand to separate. The water layer is separated, and the oil layer is fractionated to obtain refined iodobutane. Add iodobutane, solvent n-butanol, tin powder, and magnesium shavings to the reaction kettle, and react at 120 to 140°C under strong stirring. After reaching the end point, distillation is performed to recover n-butanol and unreacted iodobutane. The kettle liquid is crude butyltin iodide. Add 10% hydrochloric acid, control the temperature to 60-70°C, stir and wash for half an hour, let it stand and separate into layers, separate the waste acid liquid, and obtain refined di-n-butyltin diiodide. Add 20% caustic soda solution to di-n-butyltin diiodide, control the temperature to about 60°C while stirring, and proceed with the hydrolysis reaction. After the hydrolysis is completed, the mixture is allowed to stand for layering. After the water layer is separated, the mixture is washed with water to obtain refined di-n-butyltin oxide.
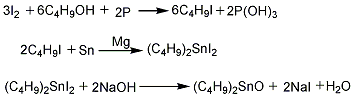
(2) Preparation of finished product Add dibutyltin oxide and maleic anhydride to the reaction kettle, control the temperature at 60 to 70°C with stirring, and perform a condensation reaction. The reaction product is dehydrated under reduced pressure and filtered to obtain the finished product.
![]()
Purpose
This product is a heat stabilizer for polyvinyl chloride, with excellent heat resistance and transparency, no sulfur pollution, and particularly good long-term heat resistance, which can prevent products from turning yellow during high-temperature processing.
This product is particularly suitable for hard transparent products. It has a higher melting point and will not reduce the softening point and impact of hard products. The general dosage is 0.5-2%. Used together with barium soap or cadmium soap, it has a synergistic effect and can further improve the stabilizing effect. Used together with dibutyltin laurate can further improve the transparency and heat resistance of the product. Used together with epoxy compounds can reduce Its tear-jerking properties. This product lacks lubricity and has poor processing performance; due to its volatility, it sometimes foams during processing; and, under the action of hydrogen chloride generated during heating, this product will translocate into fumarate ester, which is in phase with the resin. Decreased capacitance and prone to blooming. To overcome these shortcomings, many modified varieties have been developed.