dihydroxyprophylline
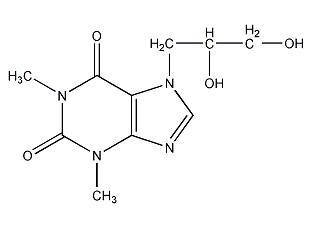

Structural formula
| Business number | 051K |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H14N4O4 |
| Molecular weight | 254.25 |
| label |
Dihydroxypropyl theophylline, 1,3-dimethyl-7-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione, 7-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)naphthyl base, 7-(2,3-Dihydroxypropyl)theophylline, 7-(2,3-Dihydroxypropyl)-1,3-dimethyl-purine-2,6-dione |
Numbering system
CAS number:479-18-5
MDL number:MFCD00005759
EINECS number:207-526-1
RTECS number:XH5100000
BRN number:284563
PubChem number:24893280
Physical property data
1. Character:White crystalline powder
2. Density (g/ m3,25/4℃): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/cm3,AIR=1): Not OK
4. Melting point (ºC):159-163.5
5. Boiling point (ºC,Normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC,5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive Index: Undetermined
8. Flash Point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific optical rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa,25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa,60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (octanol/Log value of partition coefficient for water: undetermined
17. Explosion limit (%,V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%,V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: easily soluble in water
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity: Orally administered to ratsLD:>400mg/kg, no details except lethal dose;
Rat subcutaneouslyLD50: 1253mg/kg, no details except lethal dose;
Rat transvenous LD50: 860mg/kg, no details except lethal dose;
Orally administered to miceLD50: 1954mg/kg, no details except lethal dose;
Mouse transabdominal LD50: 195mg/kg, no details except lethal dose;
Mouse subcutaneouslyLD50: 1052mg/kg, no details except lethal dose;
Mouse transvenousLD50: 1080mg/kg, no details except lethal dose.
Ecological data
This substance may be harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1、 Molar refractive index:61.49
2、 Molar volume(m3/mol):161.1
3、 Isotonic specific volume (90.2K):460.6
4、 Surface tension(dyne/cm):66.8
5、 Polarizability(10-24cm3):24.37
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 5
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 98.9
7. Number of heavy atoms: 18
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 364
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Use and store according to specifications, no decomposition will occur, and avoid contact with oxides
Storage method
Save in a sealed manner and place it in a ventilated and dry place to avoid contact with other oxides.
Synthesis method
It is obtained by condensation of theophylline sodium salt and monochloropropylene glycol.
Purpose
This product, like aminophylline, is a xanthine bronchodilator drug. It is suitable for the treatment of bronchial asthma, asthmatic bronchitis and chronic emphysema. It can also be used to prevent bronchial asthma attacks. It can also be used to treat angina pectoris and cardiac edema. Theophylline is a representative variety of xanthine drugs. In order to improve the solubility of theophylline, aminophylline (a double salt of theophylline and ethylenediamine), choline (a double salt of theophylline and choline), Dihydroxypropyl theophylline (N-7 derivative of theophylline), etc. Dihydroxypropyl theophylline is more water-soluble than aminophylline, but its effect is weaker than that of aminophylline. Its toxicity is about 1/5 of aminophylline. The oral LD50 in rats is 3400 mg/kg.