Dimethoate Dimethoate
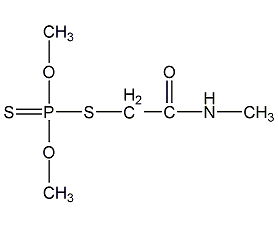

Structural formula
| Business number | 01BG |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H12NO3PS2 |
| Molecular weight | 229.26 |
| label |
Lego, O,O-dimethyl-S-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl]phosphorodithioate, Cygon, Daphene, Lurgo, O,O-Dimethyl-S-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl] phosphorodithioate, Organophosphorus pesticides |
Numbering system
CAS number:60-51-5
MDL number:MFCD00053676
EINECS number:200-480-3
RTECS number:TE1750000
BRN number:1785339
PubChem number:24868923
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: white crystals with a camphor smell. Industrial products are usually light yellow-brown emulsions. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 51~52[2]
3. Boiling point (℃) : 117 (0.013kPa) [3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.28[4]
5. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.78[5]
6. Flash point (℃): 107 (CC) [6]
7. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, chloroform, benzene, ketones, etc. [7]
Toxicological data
1. The acute daily LD50 of the pure product in rats is 500 ~ 600mg/kg, and the industrial product is 320 ~ 380mg /kg (94%} ~ 96%}). The acute transdermal LD50 in rats is 650mg/kg. The acute daily LD50 of male mallard ducks is 15mg/kg, and that of female ducks is 40mg/kg}30mg/kg). Carp L (2 is 40mg/L}48h). The LD50 of bees is 0. 09pg/bee.
2. Acute toxicity[8] LD50: 60mg/kg (rat oral); 750mg/kg (Rabbit transdermal)
3. Irritation No data available
4. Mutagenicity[9] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 5μg/dish. Sister chromatid exchange: human lymphocytes 2mg/kg. Micronucleus test: mice take 103mg/kg orally (24h). Unprogrammed DNA synthesis: human fibroblasts 100 μmol/L.
5. Teratogenicity[10] The lowest toxic dose ( TDLo) 120mg/kg, causing developmental malformations of the musculoskeletal system.
6. Others[11] The lowest oral toxic dose in rats (TDLo): 120mg/kg (pregnant 6~15 days), causing abnormal development of the musculoskeletal system. The lowest oral toxic dose in rats (TDLo): 256 mg/kg/week (intermittent), causes cancer, liver tumors, and hematological tumors.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[12] LC50: 6.2mg/L (96h) (rainbow trout, static); 6mg/L (96h) (bluegill, static); 2.5mg/L (48h) (water fleas)
2. Biodegradability[13]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 264~1344
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 1056~5376
3. Non-biodegradability[14]
Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 0.469~4.69
First-order hydrolysis half-life (h): 2822
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 54.45
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 175.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 467.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 50.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 21.58
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 5
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 5
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 105
7. Number of heavy atoms: 12
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 191
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[15] Stable
2. Incompatible substances [16] Strong oxidants, alkalis
3. Conditions to avoid contact[17] Heating
4. Polymerization hazard[18] No polymerization p>
5. Decomposition products[19] Sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, phosphorus oxides
Storage method
Storage Precautions[20] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. The industrial methods for producing dimethoate mainly include the chloroacetylmethamide method and the post-aminolysis method. The latter method was developed after the chloroacetylmethylamide method. This method has few side reactions, the product purity can reach more than 90%, and the crude product yield is about 90%.
2. The preparation of O,O-dimethyl dithiophosphate (referred to as methyl sulfide) usually uses the action of P2S5 and CH3OH, with an appropriate excess of methane, and the reaction temperature is 55-60 ℃, which is strong. Exothermic reaction, special attention should be paid to safety when operating. The reaction process is complex and a series of side reactions occur simultaneously. The yield and content of O,O-dimethyldithiophosphate is 75%-80%. Using an appropriate catalyst and reacting at (55±2)°C, the yield and content can reach about 90°C.
3. Preparation of O,O-dimethyl-5-(methyl acetate) dithiophosphate O,O-dimethyl-S(methyl acetate) dithiophosphate It is prepared by the reaction of O,O-sodium dimethyl dithiophosphate and methyl chloroacetate. The raw material ratio is 1:1.7, and the reaction temperature is 55°C. If a continuous production process is used, the preheating temperature is h0-70°C. The reaction temperature is ×80±5)°C.
4. Synthesis of dimethoate O, O-dimethyl-S-(methyl acetate) dithiophosphate a and monomethylamine, the raw material ratio is 1: (1.2-1.3) , the reaction temperature is -5-0°C. At the end of the reaction, add benzene (or vinyl chloride) to extract the dimethoate in the reaction solution, add hydrochloric acid to adjust the bamboo pH to 7, and add an appropriate amount of water to promote stratification. Specifications 40%, 50%, 80%, Dimethoate EC; 4%, Dimethoate EC for silkworms; 3.6%} Hypertonic Dimethoate EC; 2%, 3%, 10%, Dimethoate agent; 20%, 50% , dimethoate wettable powder; 10%, 50% dimethoate granules.
Purpose
1. Dimethoate is a highly effective and broad-spectrum insecticide and acaricide with contact and systemic properties. It has a higher toxic effect on a variety of pests, especially those with sucking mouthparts, and has a wide range of insecticides. It can control aphids, red spiders, leafminers, thrips, fruit flies, sawflies, planthoppers, leafhoppers, and scales. insect. Dimethoate can sneak into the body of plants and maintain its efficacy for about a week. The oral LD50 of mice is 156.3 mg/kg, the transdermal LD50 is 700-1150 mg/kg, and the intraperitoneal injection LD50 is 184 mg/kg.
2. Used as pesticide. [21]