Dimethoxymethane Dimethoxymethane
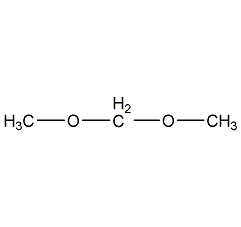
Structural formula
| Business number | 0301 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H8O2 |
| Molecular weight | 76.09 |
| label |
Methyl, Dimethyl formal, Formaldehyde dimethyl acetal, Methyl, Dimethyl formal, dimethoxymethane, Formaldehyde glycol, Methylene diethyl ether, Methylene glycol dimethyl Ether, Formaldehyde dimethyl acetal, plasticizer, hypnotic, Analgesics |
Numbering system
CAS number:109-87-5
MDL number:MFCD00008495
EINECS number:203-714-2
RTECS number:PA8750000
BRN number:1697025
PubChem number:24893265
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless, transparent and volatile liquid with an odor similar to chloroform. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -105[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 42.3[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.86[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.63[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 43.98 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1940.8[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 215[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0[9]
10. Flash point (℃): -17.8 (OC )[10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 237[11]
12. Explosion upper limit ( %): 17.6[12]
13. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.6[13]
14. Dissolution Properties: Slightly soluble in water, miscible in most organic solvents such as ethanol and ether. [14]
15. Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 0.340
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 30ºC): 0.325
17. Ignition point (ºC): 237.2
18. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol): 28.64
19. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 7.95
20. Heat of combustion (KJ/kg, constant volume): 1932.6
21. Heat of combustion (KJ/kg, constant pressure): 1935.1
22. Heat of combustion (KJ/kg, constant pressure, gas): 1992
23. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 20ºC, constant pressure): 2.18
24. Critical Density (g·cm-3): 0.357
25. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1) : 213
26. Critical compression factor: 0.207
27. Eccentricity factor: 0.290
28. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3 )0.5: 17.189
29. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1) : 6.790×109
30. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 44.970
31. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -1975.68
32. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ ·mol-1): -348.15
33. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 335.72
34. Gas phase Standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -268.11
35. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -1946.77
36. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -377.06
37. Liquid phase Standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 244.01
38. Liquid phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): -227.82
39. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1) :161.42
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity:
Rat oral LD50: 6653mg/kg; rabbit oral LD50: 5708mg/kg; mouse transdermal LC50: 57000mg/m3/7H; rabbit transdermal LD50 :>16ml/kg; rat inhalation LC50: 15000ppm;
2. Methylal can cause liver and kidney disorders, and high concentrations are narcotic. Significant irritation to mucous membranes. The maximum allowable concentration in the workplace is 3100mg/m3. The lethal concentration (in air) for rats is 46650mg/m3.
3. Acute toxicity [15]
LD50: 5708mg/kg (rabbit oral)
LC50: 46650mg/m3 (rat inhalation)
4. Irritation[16] Rabbit Eye: 100μl, moderate irritation.
5. Subacute and chronic toxicity [17] Mice inhaled 58g/m3, 7 hours a day, 2 80% died after one exposure; when inhaling 35g/m3, 7 hours a day, 15 times in 22 days, 6 out of 50 mice died. Autopsy revealed bronchopneumonia, pulmonary edema, and fatty degeneration of the myocardium, kidneys, and liver.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability[18] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3 When, the degradation half-life is 2.3d (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 19.43
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 90.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 190.8
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 19.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 7.70
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 18.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 12.4
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: relatively stable to alkali. When heated with dilute hydrochloric acid, it easily decomposes into formaldehyde and methanol; reacts with hydrogen iodide to generate sulfonated methane and formaldehyde; methylal reacts with naphthalene in the presence of sulfuric acid to generate di(α-naphthylmethane); with β- Phenethylamine reacts in the presence of hydrochloric acid to generate tetrahydroisoquinoline; it reacts with phenylmagnesium iodide to generate methyl benzyl ether.
2. Stability[19] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[20] Strong oxidants, acids
4. Conditions to avoid contact [21] Air, light
5. Hazards of aggregation[22] No aggregation
Storage method
1. Storage precautions[23] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 29°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants and acids, and avoid mixed storage. It should not be stored in large quantities or for long periods of time. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
2. Packed in plastic barrels, net weight 20kg per barrel. Store in a cool, dry, ventilated place, away from fire sources, and protected from heat, sun and moisture. Store and transport according to regulations on flammable chemicals.
Synthesis method
1. Under the catalysis of concentrated sulfuric acid, methanol and formaldehyde react in the synthesis tower. The generated methylal is distilled from the Tartin, and the Tartin temperature is controlled at 41.5-42°C. Unreacted methanol is separated from the product for recycling, and methylal with a content of more than 85% is obtained. Each ton of product consumes 1100kg of methanol and 1300kg of 37% formaldehyde. The impurities in the product methylal are mainly methanol and formaldehyde. When higher purity is required, formaldehyde can be removed by oxidation with alkaline hydrogen peroxide, and methanol can be removed by distillation with metallic sodium.
Refining method: The main impurities are methanol and formaldehyde. A small amount of formaldehyde can be removed by oxidation with alkaline hydrogen peroxide. Methanol is removed by distillation with metallic sodium. During refining, the formaldehyde is removed, washed with water, dried with anhydrous potassium carbonate or calcium chloride, filtered, and distilled with metallic sodium.
![]()
Purpose
1. Used as solvent and analytical reagent. Due to the strong anesthetic properties of the vapor, it is not suitable to be used as a general solvent. It is commonly used as plasticizer, hypnotic agent, analgesic, perfume and solvent for Grignard reaction and Reppe reaction of resin.
2. Used as solvents, analytical reagents, and organic synthesis. [24]
1. Used as solvent and analytical reagent. Due to the strong anesthetic properties of the vapor, it is not suitable to be used as a general solvent. It is commonly used as plasticizer, hypnotic agent, analgesic, perfume and solvent for Grignard reaction and Reppe reaction of resin.
2. Used as solvents, analytical reagents, and organic synthesis. [24]