Dioctyl sebacate Dioctyl sebacate
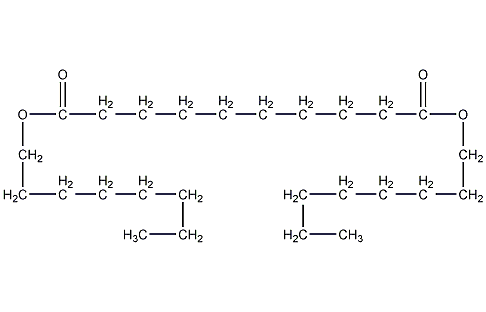
Structural formula
| Business number | 03F9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C26H50O4 |
| Molecular weight | 426.67 |
| label |
Di(2-ethylhexyl) sebacate, dioctyl sebumate, Dioctyl sebacate, Di(2-ethylhexyl) sebacate, Di-2-ethylhexyl sebacate, Dioctyl caprate, Di(2-ethylhexyl) sebum ester, diisooctyl sebacetate, Dioctyl Sebacate, Dioctyl Sebacate, Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Sebacate, Bis(2-Ethylhexyl)Decanedioate, Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) Sebacate, Sebacic Acid Dioctyl Ester, Sebacic Acid Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Ester, Sebacic Acid Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) Ester, Cold-resistant plasticizer, lubricating oil, rubber softener |
Numbering system
CAS number:122-62-3
MDL number:MFCD00009497
EINECS number:204-558-8
RTECS number:VS1000000
BRN number:1806504
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless or slightly yellow oily liquid
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 0.9119
3. Refractive index (25ºC) : 1.4496
4. Melting point (ºC): 18
5. Boiling point (ºC, 100kPa): 377
6. Boiling point (ºC, 0.53kPa) : 248
7. Boiling point (ºC, 0.13kPa): 212
8. Freezing point (ºC): -40
9. Ignition point (ºC): 57~263
10. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 19.9
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 240ºC): 666.6
12. Dissolution Properties: The solubility of this product in water is 0.02% at 20°C, and the solubility of water in this product is 0.15%. Soluble in hydrocarbons, alcohols, ketones, esters, and chlorinated hydrocarbons, but insoluble in glycols.
13. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 0.915
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat intravenous injection LD50: 900mg/kg; mouse oral LD50: 9500mg/kg
Rabbit intravenous injection LD50: 540mg/kg; guinea pig transdermal LD50: >10mL/kg
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 126.05
2, Molar volume (cm3/mol): 464.6
3, Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 1116.0
4, Surface tension (dyne/cm ): 33.2
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 49.97
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 9
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 23
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 52.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 30
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 370
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 2
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Insoluble in water and glycols, soluble in hydrocarbons, alcohols, ketones, esters, chlorinated hydrocarbons, ether and other organic solvents. It has good compatibility with resins such as polyvinyl chloride, nitrocellulose, ethyl cellulose, and rubber such as neoprene. Combustible. More stable.
Storage method
Packed in iron drums or plastic drums. Store in a cool and ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources.
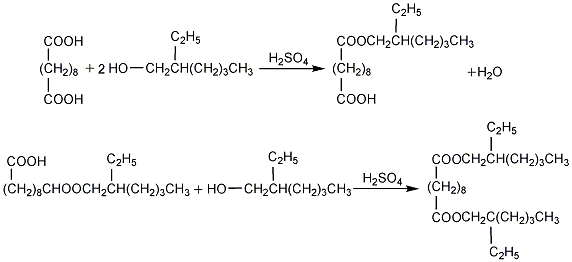
Synthesis method
1. Sebacic acid and octanol (mass ratio 1:1.6) undergo an esterification reaction under the catalysis of sulfuric acid (0.25% of the total mass of sebacic acid and octanol) to first generate monooctyl ester. In this step, the ester transformation is easier. The second step to generate diester is more difficult. It is necessary to control a higher temperature, about 130~140℃, dehydration under a vacuum of 0.093MPa, and a reaction time of 3~5 hours to obtain a high yield. The crude ester is neutralized with 2% to 5% soda ash aqueous solution, then washed with water at 70 to 80°C, and then dealcoholized under a vacuum of 0.096 to 0.097MPa. The end point is when the flash point of the crude ester reaches 205°C. The crude ester is filtered to obtain the finished product.
Refining method: vacuum distillation.

2.Stannous oxide catalytic method. In a 200mL four-necked flask equipped with a thermometer, reflux manifold, and stirrer, add measured amounts of sebacic acid, octanol (excess 15%) and 0.05% Use a catalyst to oxidize stannous. Under the protection of nitrogen, control a certain reaction temperature (200~230℃) to carry out the esterification reaction. Use a water separator to collect the water taken out by octanol. The octanol will flow back to the reaction bottle to continue participating in the reaction. . Put water into a graduated cylinder. When the water in the graduated cylinder reaches a certain amount, take a sample and titrate its acid value. If it is less than 0.2 mgKOH/g, the reaction is deemed to be completed. Otherwise, continue the reaction until it is qualified. Cool the reaction solution to 90°C, add alkaline water for neutralization and wash, let it stand for stratification, release the alkaline water, perform vacuum distillation to remove unreacted octanol in the material, and finally add activated carbon for adsorption and filtration to obtain the product DOS.
Purpose
1. Purpose: It is used as a cold-resistant plasticizer for nitrocellulose and polyvinyl chloride resin, and has good volatility resistance, light stability, electrical insulation and wettability. It can also be used as a plasticizer for a variety of synthetic rubbers, ethyl cellulose, polymethyl methacrylate, polystyrene, vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer, etc. In the aviation industry, it can be used as lubricating oil and grease for jet engines. Mainly used in PVC cable materials, films, artificial leather and other products. It can also be used in the manufacture of lubricants, precision machinery oil solvents and synthetic rubber softeners.
2.is a typical cold-resistant plasticizer, suitable for polyvinyl chloride, vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer, polymethylmethacrylate, nitrocellulose, ethylcellulose and synthetic rubber, etc. It has high plasticizing efficiency and low volatility. It has excellent cold resistance, good heat resistance, light resistance and electrical insulation. It also has good lubricity when heated, making the product look and feel good, especially Suitable for making cold-resistant wire and cable materials, artificial leather, films and adhesives, etc. However, this product has high mobility, is easily extracted by hydrocarbons, and its water resistance is not ideal. It is often used together with phthalates. The US FDA permits DOS plasticized plastic films to be used as food packaging materials.