Ethyl bromoacetate Ethyl Bromoacetate
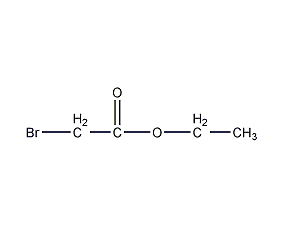

Structural formula
| Business number | 02RJ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H7BrO2 |
| Molecular weight | 167.00 |
| label |
Ethyl bromoacetate, Bromoacetic Acid Ethyl Ester |
Numbering system
CAS number:105-36-2
MDL number:MFCD00000191
EINECS number:203-290-9
RTECS number:AF6000000
BRN number:506456
PubChem number:24848125
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless to yellow liquid[1]
2. Melting point (℃): -13.8[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 158.8[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 1.51[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 5.8[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.35 (25℃ )[6]
7. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.12[7]
8. Flash point ( ℃): 47.8[8]
9. Solubility: Insoluble in water, miscible in ethanol and ether, soluble in benzene and acetone. [9]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity No data available
2. Irritation No data available
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3. Non-biodegradability[10] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105pcs/cm3, the degradation half-life is 14d (theoretical). When the pH value is 7 and 8, the hydrolysis half-life is 8d and 18h respectively (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 30.08
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 111.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 268.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 33.7
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 11.92
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 62.7
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[11] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[12] Alkalis, acids, strong oxidants, strong reducing agents
3. Conditions to avoid contact[13] Heat
4. Aggregation hazard[14] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[15] Hydrogen bromide
Storage method
Storage Precautions[16] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature does not exceed 30°C and the relative humidity does not exceed 70%. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, acids, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. First, bromine is reacted with acetic acid and acetic anhydride in pyridine to prepare bromoacetic acid, and then bromoacetic acid and ethanol are reacted in the presence of sulfuric acid to generate ethyl bromoacetate. It is generally prepared in two steps. ① Preparation of bromoacetic acid: Add 3L glacial acetic acid and 100mL acetic anhydride to the flask, then add 15g red phosphorus or 70g phosphorus tribromide, heat to 100°C with stirring, and start slowly dripping 300mL (900g, 5.6mol) from the separatory funnel ) bromine, the reaction is induced, do not add it too fast to avoid sudden reactions. After the reaction starts (HBr is released), keep it between 90 and 100°C, and then slowly drop in 2.0L bromine (total 2.3L, 41mol). After the addition, continue stirring and heating to turn the brown-red liquid into orange-red. Since then, few have been released. Recover unreacted acetic acid until the distillation temperature reaches 140°C, and recover approximately 1L for the next synthesis. ②Esterification: Pour the above crude bromoacetic acid into another 10L flask, add 5L industrial ethanol and 200mL sulfuric acid, reflux on a boiling water bath for 12 hours, recover the ethanol, wash it three times with saturated brine, dry it with anhydrous sodium sulfate and then fractionate. , collect the 154~158℃ fraction, and get 2.4~2.6kg.
2. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a water separator, add 220g (1.58mol) of bromoacetic acid (2) and 155mL of absolute ethanol (2.66mol) , 240mL toluene and 1mL concentrated sulfuric acid, and then add zeolite. Heat to reflux, water, toluene, and ethanol are separated into layers in the water separator. Toluene flows back into the reaction bottle, and the lower layer is separated, and approximately 75 mL is collected. Add another 20 mL of ethanol and continue the reflux reaction for 0.5 h. Steam off as much ethanol and toluene as possible. Pour the reactants into water and let stand to separate. Separate the aqueous layer, wash it with 5% sodium bicarbonate and water in sequence, dry it with anhydrous sodium sulfate, fractionate, collect the 164-168°C fraction, and obtain ethyl bromoacetate ① (1) 205g , the yield is 78%. Note: ① Ethyl bromoacetate has a strong tear-inducing effect, and the entire operation should be performed in a fume hood. [18]
Purpose
Used in organic synthesis to produce military poison gas. [17]