Hydroquinone Hydroquinone

Structural formula
| Business number | 03GG |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H6O2 |
| Molecular weight | 110.11 |
| label |
1,4-dihydroxybenzene, gallinol, guineas, hydroquinone, p-hydroxyphenol, 1,4-Benzodiphenol, Haider, 1,4-Dihydroxybenzen, 1,4-Benzenediol, Quinol, Hydroquinol, p-Dihydroxybenzene, Phenol, aromatic alcohols and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:123-31-9
MDL number:MFCD00002339
EINECS number:204-617-8
RTECS number:MX3500000
BRN number:605970
PubChem number:24278475
Physical property data
1. Character: white crystal[1]
2. Melting point (℃): 170.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 285[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 1.33[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.81[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (132.4℃) [6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2849.8[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃) : 549.9[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 7.45[9]
10. Octanol/ Water partition coefficient: 0.59[10]
11. Flash point (℃): 165 (CC)[11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 516[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 15.3[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.6[14]
15. Solubility: soluble in water, easily soluble in ethanol and ether. [15]
16. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.32815
17. Crystal phase Standard heat of combustion (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2854.1
18. Crystal phase standard claim heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -364.5
19. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2953.3
20. Gas phase Standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -265.3
21. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K -1): 344.28
22. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -179.6
23. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 123.60
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16] LD50: 320mg/kg (rat oral)
2. Irritation[17] Human transdermal: 2%, mild irritation; 5%, severe irritation.
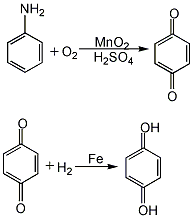
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity [18] Subacute poisoning in animals manifests as hemolytic jaundice, anemia, leukocytosis, increased red blood cell fragility, hypoglycemia, furThen add iron powder with a molar ratio of benzoquinone to benzoquinone of 1:0.7, heat to 90-100°C, and react under stirring for 3-4 hours. The product of the reduction reaction is hydroquinone. After the reduction product is filtered to remove iron oxide slag, it is dehydrated and concentrated under reduced pressure. Then add sodium metabisulfite, activated carbon, and zinc powder, and heat to boiling for decolorization. After filtering while hot, the filtrate is slowly cooled to below 30°C, and hydroquinone is precipitated as needle-shaped crystals. After centrifugal dehydration, it is added to an ebullating bed and dried at 80°C to obtain the finished product.
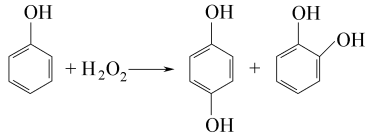
2.The phenol hydroxylation method uses hydrogen peroxide as the hydroxylating agent, and the reaction is carried out in the presence of a catalytic amount of inorganic strong acid or divalent iron salt or cobalt salt. The total reaction formula is:
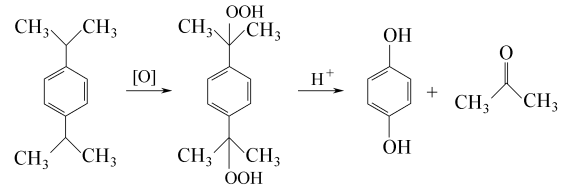
3. Dicumyl oxidation method uses peroxide to carry out oxidation reaction to produce hydroquinone. The reaction formula is as follows:

4. The method of preparing photographic grade hydroquinone is to use activated carbon to decolorize the hydroquinone solution formed by dissolving it in salt-free water, and then incubate it at 5 to 10°C It is made by recrystallizing, centrifuging and drying in a non-oxidizing atmosphere.
Purpose
1. Hydroquinone is mainly used as a developer for photography. Hydroquinone and its alkylates are widely used as polymerization inhibitors added during the storage and transportation of monomers. The commonly used concentration is about 200ppm. Hydroquinone monomethyl ether is an intermediate of edible oil antioxidant BHA; hydroquinone dimethyl ether is an intermediate of dyes, organic pigments and spices; hydroquinone diethyl ether is an intermediate of photosensitive pigments and dyes . Hydroquinone is also used to prepare N, N’-diphenyl-p-phenylenediamine, which is an antioxidant and deodorant used in rubber and gasoline.
2. Also used as photographic developer, antioxidant for rubber and gasoline, dye intermediate, etc.
3. In the treatment field, adding hydroquinone to the hot water and cooling water of the closed-circuit heating and cooling system can inhibit corrosion of metals on the water side. Hydroquinone is used as an oxygen scavenger for boiler water. Hydroquinone is added to the boiler water when it is preheated and deoxygenated to remove residual dissolved oxygen.
4. Polymerization inhibitor for styrene, butadiene, isoprene, vinyl acetate, acrylonitrile and other resins or rubber monomers. The commonly used concentration is about 200×10-6. It is also used as Preparation of black and white developers, anthraquinone dyes, azo dyes, rubber antioxidants, stabilizers and antioxidants, etc.
5. Used as a polymerization inhibitor for styrene, acrylic esters, grafted chloroprene adhesives, acrylonitrile and other vinyl monomers, and as a terminator or stabilizer for high-temperature emulsion polymerization reactions. It is also used as an antioxidant for phenolic-nitrile adhesives, a coagulant for gasoline, a developer for film, photography, and X-ray films, a rubber antioxidant, and an antioxidant for grease and phenolic-nitrile adhesives. , stabilizers for paints and varnishes, etc. It is also a raw material for the manufacture of anthraquinone dyes, azo dyes, medicines and hair dyes.
6. Used as a developer in photographic plate making and for electroplating addition.
7. Used as corrosion inhibitor, stabilizer and antioxidant in detergents, and also used as hair dye in cosmetics.
8. Preparation of black and white developer, anthraquinone dye, azo dye, rubber antioxidant, stabilizer and antioxidant. [31]