Isoquinoline
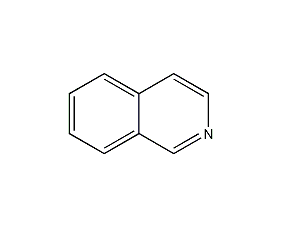

Structural formula
| Business number | 03B6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C9H7N |
| Molecular weight | 129.16 |
| label |
catalyst, iron preservative, Curing agent for soluble phenolic resin |
Numbering system
CAS number:119-65-3
MDL number:MFCD00006898
EINECS number:204-341-8
RTECS number:NW6825000
BRN number:107549
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless flaky crystals or liquid, water-absorbent, and more alkaline than quinoline. Has an odor similar to anise oil and anisole.
2. Density (g/mL, 30/4℃): 1.09101
3. Melting point (ºC): 26.48
4. Boiling point (ºC, Normal pressure): 243.24
5. Boiling point (ºC, 99.1KPa): 242.2
6. Refractive index (30ºC): 1.62078
7. Viscosity ( mPa·s, 30ºC): 3.2528
8. Flash point (ºC, closed): >107
9. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 5.61
10. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): 4702
11. Heat of generation (KJ/mol, liquid, 31ºC): 145.18
12. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg ·K), 31ºC, constant pressure): 1.47
13. Critical temperature (ºC): 530
14. Vapor pressure (kPa, 63.5ºC): 0.13
15. Body expansion coefficient (K-1, 30ºC): 0.000722
16. Solubility: can be mixed with alcohol, ether, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, acetic acid Miscible with phenyl ester, indene, oxyindene, etc. It is miscible with naphthalene in any proportion at 80°C.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 360mg/kg; rabbit dermal LD50: 180mg/kg
2. It is more toxic than quinoline and has bactericidal properties. Animal tests have shown damage to the liver.
Ecological data
Slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 42.18
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 116.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 305.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 46.6
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 16.72
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 12.9
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 111
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine chemistryNumber of bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with strong oxidizing agents.
Chemical properties: Isoquinoline is slightly more basic than quinoline (pKa 5.14). It dissolves in dilute acid to form a salt. The melting point of picric acid salt is 224~225℃. Reacts with alkyl halides to form quaternary ammonium salts. When oxidized with permanganic acid, pyridine 3,4-dicarboxylic acid and phthalic acid are generated. When isoquinoline is nitrated with mixed acid, substitution occurs at positions 5 and 8. Substitution occurs at position 4 during direct bromination. When the addition compound of isoquinoline and aluminum trichloride is brominated, substitution occurs at the fifth position.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and water. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment.
Synthesis method
Crude quinoline containing 83% quinoline, 15% isoquinoline, and 2% methylquinoline can be used as a resource for isoquinoline, but generally after cutting the crude quinoline fraction at 237.5-239.5°C, Continue to cut the fraction section at 243-246°C as the raw material for extracting isoquinoline. In this fraction, 13-28% of 2-methylquinoline and about 3.9% of quinoline are partially separated in the form of hydrochloride. The isoquinoline fraction is reacted with 98% sulfuric acid in an alcohol solution at 35%°C to form isoquinoline sulfonate. When cooled, isoquinoline sulfonate crystallizes out before its homologue sulfonate. After filtration, use 85% ethanol for recrystallization, and then decompose it with 20% ammonia water. The resulting oil layer is washed with water and then distilled to cut the 242-243°C fraction to obtain isoquinoline with a purity greater than 95%.
Refining method: Add cadmium nitrate to the fraction with a content of about 40%, and collect the resulting precipitate. It is washed with a mixture of cadmium nitrate and benzene, decomposed with 30% sodium hydroxide solution after steam distillation, and the free oil is steam distilled to obtain the pure product. The yield is 73.0% to 74.9%, and the melting point is 23.7 to 25°C. In addition, it can also be refined by the method of drying with 5A molecular sieve or anhydrous sodium sulfate and then fractionating under reduced pressure.
Purpose
Used in the production of pesticides, medicines, rubber accelerators, color film sensitizers, dyes and other products. It is used as a raw material for medicines, dyes, pesticides, anion exchange resins, etc., as a preservative for iron, and as a curing agent for soluble phenolic resin. The addition compounds formed with metals can be used for the quantitative determination of nickel and cadmium and the qualitative determination of precious metals. Isoquinoline can also be used as a catalyst in benzoylation reactions and polymerization reactions of α-olefins.