m-Dinitrobenzene m-Dinitrobezene

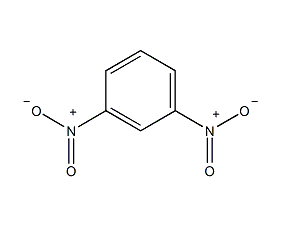
Structural formula
| Business number | 02G9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H4N2O4 |
| Molecular weight | 168.11 |
| label |
1,3-dinitrobenzene, m-Dinitrobenzene, 1,3-Dinitrobenzene, Polymerization inhibitor, Nitrogen-containing compound solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:99-65-0
MDL number:MFCD00007222
EINECS number:202-776-8
RTECS number:CZ7350000
BRN number:1105654
PubChem number:24866285
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless yellow powder, volatile. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 89[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 301 [3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.57[4]
5. Relative vapor density (Air = 1): 5.8[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): -2912.6[6]
7. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.49[7]
8. Flash point (℃): 150 (CC)[8]
9. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, benzene, etc. [9]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[10] LD50: 59.5mg/kg (rat oral); 1900mg/kg (rabbit oral Skin)
2. Irritation[11] Rabbit eyes: 100mg, causes irritation.
3. Mutagenicity[12] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 3300ng/dish. Microsomal mutagenesis: Salmonella typhimurium 50μg/dish.
4. Others[13] The lowest oral toxic dose in rats (TDLo): 224mg/kg (16 Zhou, males), affecting the testicles, epididymis, and vas deferens. The lowest oral toxic dose in rats (TDLo): 33600 μg/kg (16 weeks before mating), which affects the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[14] IC50: 0.1~0.7mg/L (72h) (algae)
2. Biodegradability[15]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 672~4320
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 48~300
3. Non-biodegradability[16]
Aqueous phase photolysis half-life (h): 554~720
Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 2077~2.10×104
Bioconcentration: BCF: 75 (fish)
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 39.34
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 113.1
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 318.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 62.6
5. Polarizability: 15.59
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Hydrogen bond donorNumber: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 91.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 12
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 175
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determined number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain atomic stereocenter Number of stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Total Number of price key units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[17] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[18] Strong oxidizing agent, strong reducing agent, strong alkali
3. Conditions to avoid contact [19] Friction, vibration, impact p>
4. Polymerization hazard[20] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[21] sup> Nitrogen oxides
Storage method
Storage Precautions[22] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the nitration of nitrobenzene with mixed acid. The crude dinitrobenzene is refined with sodium sulfite solution. The refined filtrate mainly contains sodium nitrobenzene sulfonate, which is the product of the reaction between o- and p-dinitrobenzene and sodium sulfite. When nitrobenzene is nitrated with mixed acid, dinitrobenzene accounts for about 88% of the products, ortho-dinitrobenzene accounts for 10%, and p-dinitrobenzene accounts for 2%. The separation method of isomers and the post-treatment process designed by taking advantage of the different solubility of the three in ethanol or benzene.
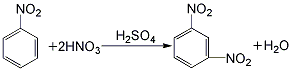
2.Under stirring, mix sulfuric acid, nitric acid and water in appropriate proportions to make it contain sulfuric acid60% and nitric acid 20% Mix the acid solution and cool it to 25°C. Slowly add 98% nitrobenzene (nitrobenzene: mixed acid = 1:2.7) with constant stirring. The temperature is first controlled below 35°C. After adding half of the nitrobenzene, increase the temperature. to 35~55℃ until the addition is complete. Then raise the temperature to 80~90℃, keep warm and stir for 1 hour:

After the reaction is completed, cool to 70°C, dilute with cold water and let stand for layering. The upper layer is crude dinitrobenzene. . Add the separated crude dinitrobenzene to about 2.5% of the 70°C alkali solution under stirring, and control the temperature not to exceed 80°C. After the addition, cool down to 65°C, and then slowly add the 95% sodium sulfite solution prepared in advance. Add slowly, control the temperature to 70-75°C, stir for 1-2 hours, and after measuring the melting point, cool down, filter out the precipitate, wash with hot water, filter after cooling, and then recrystallize with absolute ethanol to obtain the finished product.
Purpose
1. Used as a molecular polymerization inhibitor for polymerization reactions, the dosage is about 0.001% to 0.10%. This product is reduced with ammonium sulfide to form m-nitroaniline, and is reduced with a strong reducing agent to form m-phenylenediamine, which is an intermediate in dyes and organic synthesis.
2. Used as thin layer chromatography chromogenic reagent for detecting cardiac glycosides, 3-oxysteroids and D-oxysteroids. Also used in organic synthesis.
3. Used in the production of dye intermediate meta-aminoanisole. It is also used as a raw material for the production of pesticides and medicines.
4. Used in organic synthesis and dye intermediates, analytical reagents, catalysts, corrosion inhibitors, and in the manufacture of explosives. [23]