Methacrolein Methacrolein
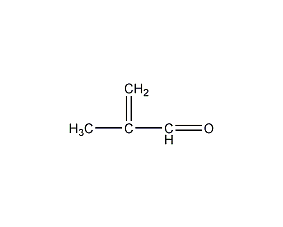

Structural formula
| Business number | 01NR |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H6O |
| Molecular weight | 70.09 |
| label |
2-Methacrolein, methacrolein, a-Methacrolein, a-Methylacrolein, Methacrylicaldehyde, Methylacrylaldehyde |
Numbering system
CAS number:78-85-3
MDL number:MFCD00006974
EINECS number:201-150-1
RTECS number:OZ2625000
BRN number:1209258
PubChem number:24848091
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless liquid with a strong irritating odor.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 0.85
3. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 0.837
4 . Melting point (ºC): -81
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 69
6. Refractive index at room temperature(n 20D): 1.4144
7. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1 ): 130.7
8. Flash point (ºC): -15
9. Specific rotation (º): Uncertain
10 . Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Uncertain
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): 16.13
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Uncertain Determine
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Uncertain
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Uncertain
15. Critical pressure (KPa ): Uncertain
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Uncertain
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
19. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, easily soluble in ethanol and ether.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity
Rat caliber LD50: 140mg/kg; rat inhalation LC50: 125PPM/4H;
Rabbit skin LD50: 430uL/kg
2. Neurotoxicity
Rabbit skin test: 2mg/24H;
Rabbit eye test: 50ug/24H;
3. Teratogenicity
Salmonella: 500 nmol/L
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 20.33
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 86.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 185.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 20.8
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.26
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.7
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 17.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 54.7
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Exist in flue-cured tobacco leaves and smoke.
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored in a cool, dark place. Storage temperature 4ºC
Synthesis method
1. A method for preparing methacrolein, using at least one of isobutylene and tert-butyl alcohol in an oxidation catalyst composition Mo12BiaCebKcFedAeBfOg, A refers to cobalt alone, or a mixture of cobalt and magnesium with an atomic ratio of magnesium to cobalt not greater than 0.7, B refers to rubidium, cesium or their mixtures, and a, b, c, d, e, f and g are the atomic ratios of bismuth, cerium, potassium, iron, A, B and oxygen corresponding to the 12 atoms of molybdenum respectively. Through the method of the present invention, high-yield methacrolein can be stably produced by using an oxidation catalyst composition. This oxidation catalyst composition has a relatively simple combination composition and can therefore be simply prepared, and it not only has excellent The thermal stability and reduction resistance extend the catalyst life and have excellent selectivity to methacrolein, wherein the catalyst composition contains bismuth, cerium, iron and potassium in specific amounts and specific relative proportions, but does not include Those ingredients that cause environmental pollution and toxicity problems, and the preparation of raw materials does not have to use compounds with low solubility in water, such as tungsten, antimony and niobium compounds. They are usually used to obtain the required catalytic properties, but their use is due to the difficulty in obtaining homogeneous catalysts. The composition is unfavorable.
2. Tobacco: FC, 40.
Purpose
Used in the manufacture of copolymers and resins, it is the raw material for the production of methyl propionic acid and the raw material for thermoplastic monomers.