Methyl acrylate Methyl acrylate
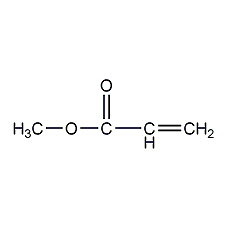

Structural formula
| Business number | 02AZ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H6O2 |
| Molecular weight | 86.09 |
| label |
2-Methyl acrylate, Acrylic acid methyl ester, Methyl propenoate, Methyl-2-propenoate, aliphatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:96-33-3
MDL number:MFCD00008627
EINECS number:202-500-6
RTECS number:AT2800000
BRN number:605396
PubChem number:24887055
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless and transparent liquid with spicy smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -76.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 80.5[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.95[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.97[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 9.1 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2102[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 263[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.3[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.8 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): -3 (OC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature ( ℃): 468[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 25.0[13]
14. Explosion Lower limit (%): 2.8[14]
15. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, easily soluble in ethanol, ether, acetone, and benzene. [15]
16. Flash point (ºC, closed): -3
17. Flash point (ºC, open): 6
18. Vapor pressure (kPa, 0ºC): 4.2
19. Vapor pressure (kPa, 20ºC): 9.3
20. Vapor pressure (kPa, 50ºC): 35.9
21. Heat of vaporization (KJ/mol): 33.2
22. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 0.53
23. Viscosity (mPa ·s, 25ºC): 0.49
24. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.4003
25. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 19.022
26. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 7.260×109
27. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1) : 49.280
28. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2098.57
29. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) )(kJ·mol-1): -333.00
30. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2069.36
31. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -362.21
32. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 160
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 277mg/kg (rat oral); 827mg/kg (mouse oral Oral); 1243mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 1350ppm (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation [17]
sup>
Rabbit transdermal: 10g/kg, causing irritation (open stimulation test).
Rabbit eye: 150mg, causing irritation.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity[18] Add acrylic acid, methanol, and expandable graphite to the flat-bottomed flask in sequence. The ratio of acrylic acid to methanol is 1.15:1. Connect the water separator and reflux condenser, place it on a magnetic heating stirrer to heat and stir, wait for a period of reaction, and then cool. Calculate the yield using the saponification method (neutralize the remaining acrylic acid with alkali solution, then add a quantitative KOH solution for saponification, and then titrate the excess KOH with a standard HCl solution to calculate the ester yield). At the same time, the ester is separated, the reaction liquid is distilled, and the 65-95°C fraction is collected to obtain the crude product. Wash with 5% NaCO3 solution until neutral, wash twice with saturated NaCl solution, dry with anhydrous NaSO4 and then distill. Collect the 72-74°C fraction to obtain the product.
5. Improved Raper method The improved Raper method is the Romhas method and the Daubatis method. The former mainly uses gaseous carbon monoxide to replace 80% of the carbon monoxide in nickel carbonyl; the latter is also called the high-pressure Raper method, which mainly uses tetrahydrofuran as the solvent.
①Improved Raper method. After the reaction of this method starts, carbon monoxide reacts with acetylene and alcohol to form acrylate. The introduced carbon monoxide replaces the carbon monoxide in nickel carbonyl, which can reduce the regeneration of nickel carbonyl and the recovery of nickel. The solvent for the reaction is alcohol. The reaction temperature is 30~50℃, the pressure is 0.1~0.2MPa, the ratio of acetylene to carbon monoxide is (1.01~1.10):1 (molar ratio), the ratio of methanol to total carbon monoxide is (1.1~3):1 (molar ratio) ). The amount of acid is maintained at 80% to 99% (molar ratio) of nickel carbonyl to inhibit the generation of chloropropionic acid. The characteristic of this method is that it operates under normal pressure and the equipment is easy to solve, but it still needs to prepare the toxic nickel carbonyl.
②High pressure Raper method. Using tetrahydrofuran as the solvent, palladium chloride as the catalyst, and copper chloride as the accelerator, the reaction is carried out at 200 to 225°C and 8.11 to 10.13MPa. The unreacted acetylene gas at the top of the reactor is recycled after washing away the acrylic acid. The acrylic acid and tetrahydrofuran solution at the bottom of the reactor is evaporated to obtain acrylic acid after the tetrahydrofuran is evaporated. The yield of acrylic acid is about 90% based on acetylene and about 85% based on carbon monoxide. Then acrylic acid is esterified with methanol in sulfuric acid or ion exchange resin medium to obtain methyl acrylate. For example, when producing higher esters above butyl ester, an acidic catalyst is used for continuous esterification; when producing ethyl acrylate, an ion exchange resin is used as a catalyst to obtain acrylate. The characteristics of this method are: using tetrahydrofuran as the solvent, the acetylene required for the reaction is first dissolved in tetrahydrofuran, which can reduce the risk of high-pressure treatment of acetylene. At the same time, nickel carbonyl is not needed and only nickel salt is used as the catalyst. However, the operating pressure of this method is high, so the equipment material requirements are high.
Purpose
1. The second monomer and adhesive used for polyacrylonitrile fiber. Acrylic fiber raw materials, coatings, plastics, resins.
2. It is an organic synthesis intermediate and a monomer of high molecular polymers, used in the manufacture of acrylic or acrylic ester solvent-based adhesives and emulsion-based adhesives. It is the second monomer of polyacrylonitrile fiber (acrylic fiber). It is a polymer obtained by copolymerizing with styrene, methyl methacrylate, butyl acrylate, etc. It is widely used as an adhesive, coating, leather and paper processing aid. wait.
3. This product is an important organic synthesis monomer and raw material. This product is the second monomer of polyacrylonitrile fiber (acrylic fiber); it can be used as plastics and adhesives; the emulsion copolymerized with butyl acrylate can well improve the quality of leather, making it soft, bright and wear-resistant. Widely used in leather industry and pharmaceutical industry.
4. Used as a monomer for synthetic polymers, the second monomer for polyacrylonitrile fibers, adhesives, etc. [30]