Methyl methacrylate Methyl methacrylate
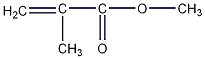
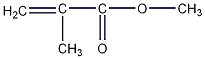
Structural formula
| Business number | 01RC |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H8O2 |
| Molecular weight | 100 |
| label |
Methyl methacrylate, α-Methyl methacrylate, 2-Methyl-2-acrylic acid methyl ester, 2-Methyl methacrylate, MMA, Methacrylic acid methyl ester, Aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives, Electronic coating raw materials and intermediates |
Numbering system
CAS number:80-62-6
MDL number:MFCD00008587
EINECS number:201-297-1
RTECS number:OZ5075000
BRN number:605459
PubChem number:24883162
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless and volatile liquid with a strong spicy taste. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -48[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 100.5[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.94 (20℃)[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air = 1): 3.45[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 3.9 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2642.9[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 294[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.3[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.38[10]
11. Flash point (℃): 10 (OC); 12.8 (OC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 421~435[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 12.5[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 2.1[14]
15. Solubility: slightly soluble in water, soluble in most organic solvents such as ethanol . [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 0.58
17. Refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.4142
18. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2779.8
19. Gas phase standard claimed heat (Enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -331.0
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 7872mg/kg (rat oral);
LC50: 78000mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation No information available
p>
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity[17] Dogs inhaling 11700ppm, 1.5h a day for 8 days can cause The animal died, and autopsy revealed fatty degeneration of the liver and kidneys.
4. Mutagenicity[18] Cytogenetic analysis: mouse lymphocytes 2202 mg/L.
5. Teratogenicity[19] The lowest toxic dose of inhalation (TCLo) in rats 6~15 days after pregnancy 109g/m3 (17min), causing developmental malformations of the musculoskeletal system.
6. Others[20] The lowest inhalation toxic concentration in rats (TCLo): 109g/kg (�Fabric is simple and low-cost than any process currently in production or under development.
5. Ethylene method: In this method, ethylene is carbonylated or hydroformylated to form a C3 carbonyl compound, which is then condensed with formaldehyde or an equivalent compound to form methyl methacrylate. The main advantage of this process is that the hydrocyanic acid by-product produced can be recycled as a raw material for producing ACH, and no ammonium sulfate product is produced.
6. Preparation method:
p>
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, reflux condenser, temperature base, and dropping funnel, add 75g of tricresyl phosphate, 9g of phosphorus pentoxide, and 0.2g of copper powder. Heat the oil bath to 65°C with stirring, slowly add 25g (0.2mol) of 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid methyl ester (2) dropwise, and control the reaction temperature not to exceed 65°C. After the addition is completed, raise the temperature to 80-100°C and maintain this temperature for reaction for 3 hours. Change to a distillation device to steam out the fraction below 170°C. The distillate is washed with 10% sodium carbonate solution, dried over anhydrous sodium phosphate, added with a small amount of copper powder ① and re-distilled, and the fractions at 97-100°C are collected to obtain methyl methacrylate ② (1) 16~18g. The yield is 76% to 88%. Note: 1. The purpose of adding copper powder is to prevent the polymerization of methyl methacrylate. A small amount of sulfur or diphenylamine can also be added. 2. Methyl methacrylate can also be synthesized from acetone, sodium cyanide and methanol as raw materials. [30]
Purpose
1. Used in the manufacture of organic glass, coatings, lubricant additives, wood sizing agents, paper polishes, etc.
2. Methyl methacrylate is not only an organic chemical raw material, but also can be directly used as a chemical product. As an organic chemical raw material, it is mainly used in the production of organic glass (polymethyl methacrylate, PM-MA), the manufacturing of polyvinyl chloride additives ACR, and as the second monomer in the production of acrylic fiber. In addition, it has also been widely used in adhesives, coatings, resins, textiles, papermaking and other industries. As a chemical product, it can be directly used in leather, ion exchange resins, paper polishes, textile printing and dyeing auxiliaries, leather treatment agents, lubricating oil additives, crude oil pour point depressants, wood and soft wood sizing agents, and motor coil Penetrating agent, plasticizer for insulating potting materials and plastic emulsions, floor polishing, unsaturated resin modification, advanced methacrylic acid esters and many other fields.
3. Organic synthesis monomers. It is also used in the manufacture of other resins, plastics, coatings, adhesives, scale inhibitors and dispersants, lubricants, wood sizing agents, motor coil saturating agents, paper polishes, printing and dyeing auxiliaries and insulation filling materials.
4. Used as a monomer of organic glass, and also used in the manufacture of other resins, plastics, coatings, adhesives, lubricants, wood and cork sizing agents, paper polishes, etc. [29]