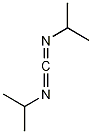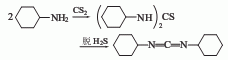
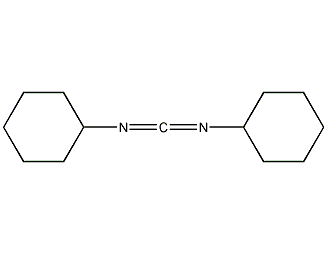
Structural formula
| Business number |
05JH |
| Molecular formula |
C13H22N2 |
| Molecular weight |
206.33 |
| label |
DCC,
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide solution,
Ester cyclic compounds and their derivatives
|
Numbering system
CAS number:538-75-0
MDL number:MFCD00011659
EINECS number:208-704-1
RTECS number:None
BRN number:610662
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Appearance: White crystal or yellowish transparent liquid
2. Density (g/ cm3, 25/4℃): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/cm3, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 34~35
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 154-156
6. Boiling point (ºC, 8kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Not determined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 55.1ºC): Undetermined
13 . Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. The logarithmic value of the oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. The upper limit of explosion (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion Lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Easily soluble in dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile and N,N-Dimethylformamide.
Toxicological data
None yet
Ecological data
This substance may be harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 63.46
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 194.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 486.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 39.2
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 25.16
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 4.7
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 24.7
7. Number of heavy atoms: 15
8. Surface charge:0
9. Complexity: 201
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determined number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Uncertain number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Use and store according to specifications. It will not decompose and avoid contact with oxides.
2. It is highly irritating to the skin. Wear rubber gloves when using it and operate it in a fume hood. This reagent easily absorbs moisture and should be stored in a desiccator.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Protect from direct sunlight. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from acids and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Dicyclohexylthiourea method: Industrially, N,N’-dicyclohexylthiourea is produced by the reaction of cyclohexylamine and carbon disulfide, which is obtained by dehydration of hydrogen sulfide.
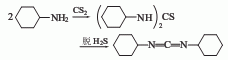
2. Dicyclohexylamine urea The method can also be obtained by reacting N,N’-dicyclohexylurea and phosphorus pentoxide in pyridine.

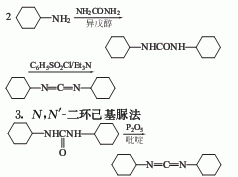
4.Preparation of N,N’-dicyclohexylamine
Mix 240 grams (2.42 mol) cyclohexylamine and 60 grams (1.00 mol) urea in 480 ml The reaction was refluxed in isoamyl alcohol for 20 hours. After cooling, the crystals were filtered out, washed with diethyl ether, and dried to obtain 200 grams of N, N’-dicyclohexyl peptide with a yield of 89%.
5. Preparation of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
Put 200 grams (0.891 mol) of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide Pulse, 300 grams (1.574 mol) of toluene sulfonyl chloride in 600 ml of anhydrous pyridine and stir at 70°C for 1 hour. The reaction mixture was poured into 1.5 kg of crushed ice and extracted with diethyl ether. The ether solution was washed with water and dried. The diethyl ether was evaporated and the residue was evaporated under reduced pressure. 152 g (82%) of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide was obtained.
Purpose
1. Used for the synthesis and dehydration of amikacin and amino acids. It is a good low-temperature biochemical dehydration agent and also used for the synthesis of acids, anhydrides, aldehydes, ketones, etc. In Japan, dehydrating agents for glutathione account for 90% of total consumption. When this product is used as a dehydration condensation agent, it can be reacted in a short time at room temperature. The product after the reaction is dicyclohexyl urea. Since the product has very little solubility in organic solvents, the reaction product is easy to separate; at the same time, since the product is difficult to dissolve in water, the reaction can still proceed even in an aqueous solution. This product is also used in the synthesis of peptides and nucleic acids. Using this product, peptides can be easily synthesized from compounds with free carboxyl groups and compounds with free amino groups at room temperature, and the yield is very high. Used to produce vasopressin and cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
2. 1,3-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) is a strong dehydrating reagent, mostly used in the synthesis of amides, esters and acid anhydrides. At the same time, DCC oxidizes alcohol to ketone, primary amide to nitrile, and β-hydroxyketone to α,β-unsaturated ketone. reaction has been widely used.
Synthesis of amides, esters, acid anhydrides, etc. (dehydrating agent) DCC is commonly used in peptide synthesis and in compounds where amines react with carboxylic acids to form amide bonds. The reaction yield is Higher, the reaction rate is also faster (Formula 1)[1].

In the synthesis of esters, primary Alcohols, secondary alcohols, alkylthiols, etc. can all undergo coupling reactions with carboxylic acid compounds in the presence of DCC. For alcohols with greater steric hindrance, the reaction yield is relatively low (Formula 2)[2]. Phosphate esters [3] can also be synthesized by DCC coupling.

For the synthesis of acid anhydrides, the DCC is One of the simplest coupling reagents with the mildest reaction conditions and the highest yield[4].
Conversion of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones In the presence of DCC, DMSO can be activated and react with primary or secondary alcohols to generate the corresponding aldehydes or ketones, thereby realizing the conversion from alcohols to aldehydes or ketones. Conversion to aldehydes or ketones (Formula 3), compared with other metal-catalyzed oxidation reactions, the oxidation reaction conditions in the presence of DCC are extremely mild, the product is single, and it has good chemical selectivity[5].

Dehydration reaction DCC has strong dehydration properties, so it is often used to synthesize compounds with certain special functional groups, such as the reaction of using carboxylic acid to synthesize enone (Formula 4)[6 ]. β-hydroxyketone, β-hydroxyester, etc. can react with DCC to generate α, β-unsaturated ketone or ester.

Conversion of Thiourea to Cyanoguanidine Under the action of DCC, thiourea can be converted into cyanoguanidine (Formula 5) [7] under appropriate reaction conditions.

Carboxylic Acids and the NHS The reaction forms an activated ester Under the coupling of DCC, the carboxylic acid reacts with NHS to form an activated ester (formula 6)[8], and then the nucleophilic attack of the amino or hydroxyl group on the carbonyl group forms an amide bond or ester bond.

It is converted into cyanoguanidine (Formula 5)[7] under the reaction conditions of �.

Carboxylic Acids and the NHS The reaction forms an activated ester Under the coupling of DCC, the carboxylic acid reacts with NHS to form an activated ester (formula 6)[8], and then the nucleophilic attack of the amino or hydroxyl group on the carbonyl group forms an amide bond or ester bond.