Nitrile Butyroiutrile
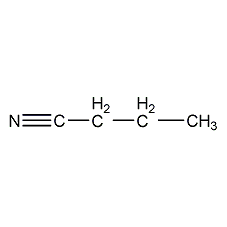
Structural formula
| Business number | 02ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H7N |
| Molecular weight | 69.11 |
| label |
n-butyronitrile, n-Butyronitrile, Nitrile C4, Propyl cyanide, Nitrogen-containing compound solvents, aliphatic compounds, synthetic raw materials, Intermediates |
Numbering system
CAS number:109-74-0
MDL number:MFCD00001968
EINECS number:203-700-6
RTECS number:ET8750000
BRN number:1361452
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with pungent odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -112[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 117.5[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.80[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.4[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 2.0 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2568.68[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 309.1[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.8[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.53 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): 24 (OC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃ ): 501[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 11.4[13]
14. Explosion lower limit (%): 1.65[14]
15. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, miscible in ethanol, ether, dimethylformamide, soluble in benzene. [15]
16. Refractive index (15ºC): 1.3860
17. Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 0.624
18. Viscosity (mPa·s, 30ºC): 0.515
19. Flash point (ºC): 501
20. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 37.01
21. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 5.02
22. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC): -5.82
23. Solubility (% ,25ºC, water): 3.3
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 50mg/kg (rat oral); 27.7mg/kg (mouse Oral); 400mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 702mg/m3 (mouse inhalation, 1h)
2 . Irritation[17]
Rabbit transdermal: 395mg, mild irritation (open irritation test).
Rabbit eye: 500mg (24h), mild irritation.
3. Others[18] The minimum toxic concentration (TCLo) for inhalation in rats: 200ppm (6h) (gestation 6~20d), causing embryonic damage toxicity.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability[19] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3 When, the degradation half-life is 32d (theoretical��).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 20.49
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 87.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 199.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 26.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.12
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 23.8
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 47.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[20] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[21] Strong acid, strong alkali, strong reducing agent, strong oxidizing agent
3. Polymerization hazard[22] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[23] Store in a cool, well-ventilated special warehouse, and implement the “two people to send and receive, and two people to keep” system. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from reducing agents, acids, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the oxidation of butene and ammonia
![]()
2. Obtained from the catalytic oxidation of butanol and ammonia.
![]()
3. Mixed with hydrocarbons In this case, acetonitrile can be added and removed by azeotropic distillation. If it contains isonitrile impurities, use concentrated hydrochloric acid to decompose and remove them. Moisture is removed with magnesium sulfate or phosphorus pentoxide. Finally refined through distillation.
Purpose
1. Used as intermediates, raw materials for organic synthesis, solvents, and other fine chemicals.
2. Used as chemical drugs and pharmaceutical intermediates. [24]