p-Aminophenol p-Aminophenol
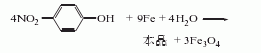
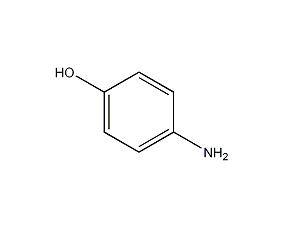
Structural formula
| Business number | 03GF |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H7NO |
| Molecular weight | 109.13 |
| label |
4-aminophenol, 4-amino-1-hydroxybenzene, 4-Hydroxyaniline, P-aminophenol, p-hydroxyaniline, 1-Amino-4-hydroxybenzene, 4-Amino-1-hydroxybnzene, 4-Aminobenzenol, 4-Aminophenol, Rodinal, Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:123-30-8
MDL number:MFCD00007869
EINECS number:204-616-2
RTECS number:SJ5075000
BRN number:385836
PubChem number:24861974
Physical property data
1. Character: white to grayish brown crystal[1]
2. Melting point (℃): 186~189[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 150 (0.4kPa) [3]
4. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.4 (150℃)[4]
5. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.04[5]
6. Solubility: slightly soluble In water, ethanol, ether. [6]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[7]
LD50: 375mg/kg (orally in rats); 420mg/kg (orally in mice); 10000mg/kg (orally in rabbits); >10g/kg (transdermally in rabbits).
LC50: >5mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 1h)
2. Irritation[8] sup>
Rabbit transdermal: 12500μg (24h), mild stimulation.
Rabbit eye: 100mg, mild irritation.
3. Mutagenicity [9] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 2μmol/dish. Somatic mutation: mouse lymphocytes 4mg/L. Sperm morphology: mouse abdominal cavity 500mg/kg (5d). DNA damage and inhibition: human lymphocytes 250 μmol/L.
4. Teratogenicity[10] The lowest toxic dose (TDLo) of 100mg/kg was administered intravenously to hamsters on the 8th day after pregnancy, causing teratogenicity to the central nervous system, Developmental malformations of the eyes, ears, and musculoskeletal system.
5. Others[11] The lowest toxic dose in rats (TDLo): 563mg/kg (gestation 1~22d), stillbirth.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[12]
LC50: 24mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow); 2mg/L (48h) ) (goldfish)
EC50: 0.032mg/L (water flea)
2. Biodegradability [13] When the COD value of 4-aminophenol is 200 mg/L, domesticated activated sludge is used, and the sludge concentration reaches 100 mg/L. After 5 days (aerobic), the COD removal rate is 87%.
3. Non-biodegradability[14] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105 pieces/cm3, the degradation half-life is 5h ( theory).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 32.37
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 90.1
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 248.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 57.4
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 12.83
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 4
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 46.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 66.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Solubility in water: 0.39% at 13℃, 0.65% at 24℃, 0.80% at 30℃, 1.5% at 50℃, 4.7% at 80℃, 8.5% at 96℃. Solubility in methyl ethyl ketone: 9.3% at 58.5°C. Solubility in absolute ethanol: 4.5% at 0°C. Soluble in hot water and ethanol, slightly soluble in water and methyl ethyl ketone, insoluble in benzene, toluene and chloroform.
2. Stability[15] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[16] Acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, chloroform, strong oxidants
4. Conditions to avoid contact[17] Heating
5. Polymerization hazard[18] No polymerization
Storage method
1. Packed in iron drums, paper drums or fiberboard drums lined with plastic bags, with a net weight of 35kg, 40kg or 50kg per drum. Store away from light, heat and moisture. Store and transport according to regulations on toxic and dangerous goods.
2. Storage precautions [19] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Iron powder reduction method Obtained from the reduction of p-nitrophenol. Raw material consumption quota: nitrophenol (industrial product) 1388kg/t, iron powder 1778kg/t, 30% hydrochloric acid 200kg/t.
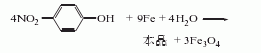
2. Phenol nitrosation method is produced by Phenol is obtained by nitrosation, reduction and acid precipitation.
3. Coupling reduction method: Using aniline as raw material, it is obtained by diazotization, coupling and reduction with iron powder.
4. The catalytic hydrogenation method of nitrobenzene mostly uses platinum, palladium or both as catalysts, and is hydrogenated and reduced to phenylhydroxylamine in 10-20% sulfuric acid aqueous solution, and then translocated to p-aminophenol, yield 70-80%. Adding surfactants to the reaction system has a certain effect on improving the yield. 5. Electrolytic reduction method of nitrobenzene. Japan’s Mitsui Touga Fine Chemicals Co., Ltd. uses electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in sulfuric acid solution and translocation of phenylhydroxylamine into p-aminophenol. In June 1977, the company built a plant in the Omuta factory. A set of 1,000 tons/year equipment.
Purpose
1. Used to produce sulfide blue FBG, weakly acidic bright yellow 5G and other dyes, to manufacture drugs such as paracetamol and clofibrate, and also to make developers, antioxidants, etc.
2. This product is an intermediate for fine chemicals such as medicines and dyes. Used in the production of paracetamol, azo dyes, sulfur dyes, acid dyes, fur dyes, developers, antioxidants and petroleum additives.
3. Test fee. Determination of copper, iron, magnesium, vanadium, nitrite and cyanate. Antioxidants. Organic Synthesis. Photographic developer.
4. Used as analytical reagents, antioxidants, oil additives, dyes, medicines, and photographic developers.
5. Mainly used in the dye industry to manufacture azo dyes, sulfur dyes, acid dyes and fur dyes (such as fur brown P). In the pharmaceutical industry, it is used to make drugs such as paracetamol and clofibrate, as well as developers, antioxidants and petroleum additives. In the cosmetics industry, used in hair dye formulations (as compound dyes).
6. Used in the manufacture of dyes, drugs and plastic curing agents. [20]