Tri-n-propylamine Tri-n-propylamine
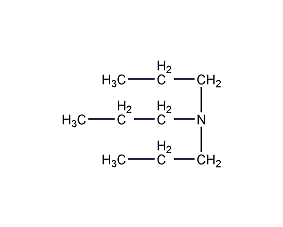
Structural formula
| Business number | 02MB |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C9H21N |
| Molecular weight | 143.27 |
| label |
None yet |
Numbering system
CAS number:102-69-2
MDL number:MFCD00009363
EINECS number:203-047-7
RTECS number:TX1575000
BRN number:1098331
PubChem number:24889818
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with ammonia odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -93.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 155~158[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.756[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 4.9[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.386 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -6335.7[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 320.9[ 8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 2.23[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.79[10]
11. Flash point (℃): 29[11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃) :180[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 5.6[13]
14. Explosion lower limit ( %): 0.7[14]
15. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ether, easily soluble in ethanol. [15]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 96mg/kg; rat inhalation LC50: 5100mg/m3/4H; mouse inhalation LC50: 3800mg/m3/2H; rabbit skin contact LD50: 570μL/kg; lactation Animal inhalation LC50: 5100mg/m3; mammalian route unknown LD50: 740mg/kg.
2. It is irritating to eyes, mucous membranes or skin, and may cause burns. Easily absorbed through skin upon contact with skin. Toxic or its vapors are toxic. The maximum allowable concentration in the workplace is 2mg/m3.
3. Acute toxicity [16]
LD50: 96mg/kg (rat oral); 570μl (433mg )/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 5100mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 4h)
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability No information available
4. Other harmful effects[17] This substance is harmful to the environment and should be treated with special Pay attention to water pollution.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 47.46
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 184.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 415.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 25.9
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 18.81
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 6
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 3.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity:47.5
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determined number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units :1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[18] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[19] Strong oxidants, acids
3. Conditions to avoid contact[20] Heating
4. Polymerization hazard[21] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[22] Amine
Storage method
Storage Precautions[23] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants and acids, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
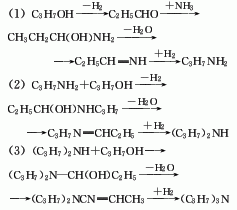
Using n-propanol as raw material under the action of Ni-Cu-Al2O3 catalyst, it is dehydrogenated to generate propionaldehyde, which is then added with ammonia, dehydrated and hydrogenated to generate propylamine, which is then repeatedly dehydrated and hydrogenated to generate dipropylamine and tripropylamine. propylamine. The reaction temperature is (210±10)℃ and the pressure is 396.66kPa. The space velocity of n-propanol is 0.25-0.51L/L·h-1. The raw material ratio is alcohol: ammonia: hydrogen = 4:2:4. The conversion rate of n-propanol is 75%-83%, and the total yield of di- and tripropylamine is 75%-80%, of which dipropylamine is 37%-41% and tripropylamine is 35%-40%. Raw material consumption quota: propanol 3500kg/t, ammonia 500kg/t, hydrogen 1200m3.

Purpose
1. Used in pharmaceuticals, pesticides, rubber and fiber processing aids, etc. Used for the synthesis of perfluorinated artificial plasma and petrochemical quaternary ammonium molecular sieve catalysts. It also has important uses in laser technology.
2. It is an organic synthesis intermediate and is used to prepare perfluorinated artificial plasma and petrochemical quaternary ammonium molecular sieve catalysts. [24]