Triethylamine Triethylamine
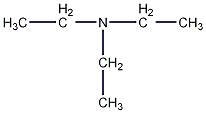

Structural formula
| Business number | 03DK |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H15N |
| Molecular weight | 101.19 |
| label |
N,N-diethylethylamine, Triethylamine, N,N-Diethyl-amine, Triethylamine, Hydrogen chloride collector, Nitrogen-containing compound solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:121-44-8
MDL number:MFCD00009051
EINECS number:204-469-4
RTECS number:YE0175000
BRN number:605283
PubChem number:24899917
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless oily liquid with strong ammonia odor. [1]
2. pH value: 11.9 (1% solution, calculated value) [2]
3. Melting point (℃): -114.8[3]
4. Boiling point (℃): 89.5[4]
5 .Relative density (water=1): 0.73[5]
6. Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.5[6]
7. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 7.2 (20℃)[7]
8. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -4334.6[8]
9. Critical temperature (℃): 262.45[9]
10. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.032[10]
11. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.45[11]
12. Flash point ( ℃): -7 (OC)[12]
13. Ignition temperature (℃): 232~249[13]
14. Explosion upper limit (%): 8.0[14]
15. Explosion lower limit (%): 1.2[15]
16. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in most organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, acetone and so on. [16]
17. Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 0.394
18. Viscosity (mPa·s, 30ºC): 0.323
19. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 20ºC): 35.89
20. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 32.13
21. Heat of generation ( KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid): -134.27
22. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 20ºC, liquid): 4340.9
23. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K ), 25ºC, constant pressure): 2.21
24. Boiling point rising constant: 3.45
25. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1): 0.00126
26.pKa (25ºC, water): 11.01
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[17]
LD50: 460mg/kg (rat oral); 570μl (416.1mg)/kg (Rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 6g/m3 (Mouse inhalation)
2. Irritation[18] Rabbit eye 250μg (24h), severe irritation.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity [19] Rabbit inhaled 420mg/m3, 7 hours each time, 5 times a week, 6 weeks later, lung congestion, hemorrhage, peribronchitis, myocardial degeneration, liver and kidney congestion, degeneration, and necrosis were seen.
4. Others[20] The lowest oral toxic dose in rabbits (TDLo): 6900μg/kg (gestation 1~3d), which is harmful to development influential.
Ecological data
1��Dyes; spices; drugs; high-energy fuels and liquid rocket propellants, etc. Used as a capture agent for acids, especially hydrogen chloride.
2. Can be used as a solvent. Used together with organotin compounds as a catalyst in the manufacture of polyurethane foam. It can be used as a catalyst for the production of polycarbonate by the phosgene method, a polymerization inhibitor for tetrafluoroethylene, a rubber vulcanization accelerator, a special solvent for paint strippers, surfactants, ion exchange resins, preservatives, bactericides, dyes, and spices. , enamel anti-hardening agent, pharmaceuticals, high-energy raw materials, liquid rocket propellant, etc.
3. Used in the preparation of quaternary ammonium compounds. Used as synthetic catalyst raw materials, solvents, penetrants, waterproofing agents, and rubber vulcanization accelerators.
4. Used as a curing agent for epoxy resin, the reference dosage is 10 to 15 parts by mass, and the curing condition is 100°C/1h. It is also used as a catalyst for the synthesis of polycarbonate by the phosgene method, a paint stripper for anionic electrophoretic coatings, a rubber vulcanization accelerator, a tetrachlorethylene polymerization inhibitor, an enamel anti-hardening agent, a high-energy fuel additive, a pesticide emulsifier, and a polyurethane polymerization accelerator. , coating anti-coagulants, etc. It is also a raw material for manufacturing pesticides, medicines, surfactants, ion exchange resins, dyes and spices, etc.
5. Used as solvent, polymerization inhibitor, preservative, and synthetic dye, etc. [29]