Vinyl acetate Vinyl acetate
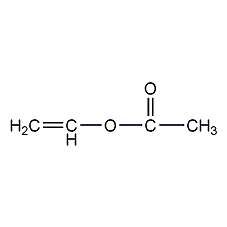
Structural formula
| Business number | 02WA |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H6O2 |
| Molecular weight | 86.09 |
| label |
Ethylene acetate, Acetic acid vinyl ester, Acetic acid ethenyl ester, Vinyl ethanoate, Rubber and plastic additives, Extracting agent |
Numbering system
CAS number:108-05-4
MDL number:MFCD00008713
EINECS number:203-545-4
RTECS number:AK0875000
BRN number:1209327
PubChem number:24869714
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless and transparent liquid with fruity aroma. [15]
2. Melting point (℃): -93.2[16]
3. Boiling point (℃): 71.8~73[17]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.93 (20℃)[18]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.0[19]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 15.33 (25℃)[20 ]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1953.6[21]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 252 [22]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.25[23]
10. Octanol/water distribution Coefficient: 0.73[24]
11. Flash point (℃): -8 (CC); 0.5~0.9 (OC)[25]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 402[26]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 13.4[27]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 2.6[28]
15. Solubility: slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, Most organic solvents such as ether, acetone, benzene, and chloroform. [29]
16. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2116.77
17. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -314.80
18. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 18.425
19. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 7.260× 109
20. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 49.280
21. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2081.96
22. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ· mol-1): -349.62
23. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 327.98
24. Liquid phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): -227.82
25. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1):155.9
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[30]
LD50: 2900mg/kg (rat oral); 2500mg/kg (rabbit dermal )
LC50: 11400mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation [31] sup>Human eye: 22ppm, causing irritation.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity [32] Rat inhalation 2.4mg/m3, 24h, mild Changes in liver enzymes.
4. Mutagenicity [33] Micronucleus test: human lymphocytes 500 μmol/L. Cytogenetic�
3. It is a synthetic monomer for organic and polymer adhesives with extremely wide uses. Used to make polyvinyl acetate emulsion (white latex); copolymerized with ethylene to make EVA resin and VAE emulsion; copolymerized with vinyl chloride to make chlorine vinegar emulsion and chlorine vinegar resin; solvent polymerized to make 4115 advanced construction adhesive; copolymerized with butyl acrylate to make Acetylene-acrylic emulsion; copolymerized with butyl acrylate in a solvent to prepare building sealant; used as a hard monomer to make acrylic emulsion; grafted with styrene-butadiene rubber to make PVC wood grain film adhesive. It is also the main raw material for the production of polyvinyl alcohol and vinylon. Manufacture of adhesives, emulsifiers, fabric finishing agents, coatings, paper coatings, cement additives, food antiseptic coatings, food packaging films, chewing gum bases, cosmetic additives, etc. through solution or emulsion polymerization.
4. This product is the monomer of polyvinyl acetate and the raw material of polyvinyl alcohol resin. It can also form copolymers with other monomers and can produce water treatment chemicals, rubber, coatings, and adhesives. and other fine chemicals, etc.
5. The main application of vinyl acetate in organic chemistry focuses on enzyme-catalyzed acetyl transfer reactions. It has many other reactions, but some can be replaced by other better reagents, and some require further exploration.
Due to the special structure of vinyl acetate, the acetyl group shows higher reactivity. Moreover, many biological enzymes can catalyze the acetyl transfer reaction between vinyl acetate and other alcohols to generate new acetate esters. Acetyl transfer reactions catalyzed by biological enzymes are generally carried out under very mild conditions and exhibit a high degree of stereoselectivity and regioselectivity. For example: using racemic alcohol and vinyl acetate to react under the catalysis of a suitable biological enzyme, only one enantiomer is selectively ethyl esterified, thereby achieving the purpose of chiral resolution (Formula 1) [1~4]. Another example: When a molecule containing multiple hydroxyl functional groups reacts with vinyl acetate under the catalysis of a suitable biological enzyme, only one hydroxyl group is selectively ethyl esterified, making the regioselective reaction of a complex system extremely simple (Equation 2 )[5,6].
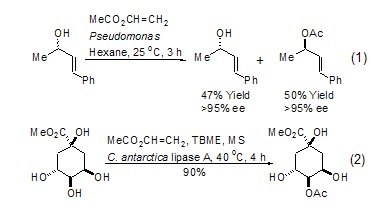
Although vinyl acetate is used in many Under such catalytic conditions, vinyl transfer reactions can occur with other acids to generate new vinyl esters[7]. However, vinyl transfer reactions using metallic iridium catalysts have recently been reported to give very satisfactory results (Equation 3)[8].
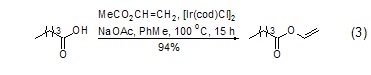
Under the action of transition metal catalyst , using simple chemical reactions [9] or electrochemical reaction conditions [10], vinyl acetate can undergo an arylation reaction of olefins with halogenated aromatic compounds. Interestingly, good results can also be obtained using chlorinated aromatics in this reaction (Eq. 4).
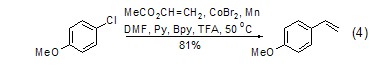
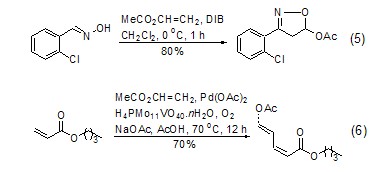
Ethylene in vinyl acetate molecule The [2+3][11,12] or [2+4][13] reaction of heteroatoms occurring in the base has relatively important synthetic significance (Formula 5) . Recently, it was reported that a cross-coupling reaction between vinyl acetate and acrylate was catalyzed by metal palladium, and the diene product was obtained with high yield and high selectivity. This is a result worthy of attention (Formula 6)[14 ].

6. Used in organic synthesis, Mainly used for synthetic vinylon, also used in adhesive and coating industries. [44]