Terephthalic Acid Terephthalic Acid
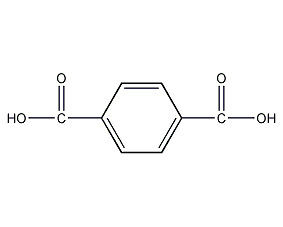
Structural formula
| Business number | 02HG |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H6O4 |
| Molecular weight | 166.13 |
| label |
1,4-phthalic acid, terephthalic acid, Pine oil phthalic acid, Pure terephthalic acid, Benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid, Acide terephtalique, Acideterephtalique, Tephthol, p-Phthalic acid, Aromatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives, organic insulating materials, acidic solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:100-21-0
MDL number:MFCD00002558
EINECS number:202-830-0
RTECS number:WZ0875000
BRN number:1909333
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: white crystal or powder.
2. Density (g/mL, 20℃): 1.51
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): >300
5. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3329.50
6. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -717.89
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash Point (ºC): 260
9. Crystal phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3189.42
10. Crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -816.13
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, 20ºC): <0.01
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, Insoluble in carbon tetrachloride, ether, acetic acid and chloroform, slightly soluble in ethanol, soluble in alkali solution.
20. Boiling point (ºC): 392.4
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation: Standard Dresser test: rabbit eye contact, 500mg/24 HREACTION SEVERITY, slight reaction; 2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: >6400mg/kg; mouse oral LD50: 3200mg/ kg; Mouse peritoneal cavity ld50: 1430mg/kg; dog venous injection LDLO: 767 mg/kg; 3. Other multiple dose toxicity: Rat via the mouth TDLO: 364mg/kg/1Y-C; rats inhaled TCLO: 5 mg: 5 mg: 5 mg: 5 mg: 5 mg: 5 mg: 5 mg /m3/2H/26W-I; Mouse oral TDLo: 5964 mg/kg/7D-I;
Ecological data
This substance is harmful to the environment and can cause pollution to water bodies and the atmosphere. Organic acids can easily form acid rain during atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physical changes. Therefore, when the pH value drops below 5, it will cause serious harm to animals and plants, and the reproduction and development of fish will be seriously affected. Metals in the soil and water sediments in the watershed can be dissolved into the water and poison the fish. Acidification of water bodies will also lead to changes in the composition and structure of aquatic organisms. Acid-resistant algae and fungi will increase, while root plants, bacteria and vertebrates will decrease, and the decomposition rate of organic matter will decrease. Acidification will seriously lead to the reduction or death of fish in lakes and rivers.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 40.11
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 114.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 331.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 70.3
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 15.90
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 74.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 12
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 169
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with strong oxidants and alkali.
2. This product has low toxicity, and its toxicity is basically the same as that of phthalic acid. Oral LD for rats is 6.0g/kg. The lethal dose injected into the peritoneal cavity is 800mg/kg. It is not as irritating to the skin as phthalic acid and does not show sensitization. Allergic symptoms, wheezing, ulcers, etc. that occur during the production process are caused by impurities in the raw materials. They can also be decomposed and detoxified in the body like phthalic acid. For those with allergies, contact with this product may cause rash or bronchial asthma or bronchitis. It is advisable to wear a dust mask during operation. The maximum allowable concentration in the air is 0.1mg/m3.
3. Exist in tobacco leaves and smoke.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. They should be stored separately from oxidants and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Packed in plastic bags, cloth bags or polypropylene woven bags, 20kg per bag. Store in a cool, ventilated and dry place. Protect from heat, sun and moisture. Store and transport according to general flammable chemical regulations.
Synthesis method
1. The most widely used and economical production method in industry is the high-temperature liquid phase oxidation method using paraxylene as raw material. Other production methods of terephthalic acid include low-temperature oxidation of p-xylene, phthalic anhydride translocation method, toluene oxidative disproportionation method, etc. 1. Paraxylene high-temperature oxidation method. Paraxylene uses acetic acid as the solvent, cobalt acetate-manganese acetate as the catalyst, and tetrabromoethane as the cocatalyst. It is oxidized at 221-225°C and 2.5-3.0MPa to form terephthalene. Formic acid. The solubility of terephthalic acid in acetic acid is not large, and the oxidation product is in the form of mud. After centrifugation and drying, crude terephthalic acid is obtained. The most harmful impurity is p-carboxybenzaldehyde, with a content of 1000-5000ppm. The crude product is dissolved in water at 280-290°C and about 7MPa pressure, and then hydrogenated in the presence of a catalyst to remove p-carboxybenzoic acid. After crystallization, filtration, washing and drying, fiber grade terephthalic acid is obtained. . 2. The low-temperature oxidation method of p-xylene uses the raw material p-xylene in an acetic acid solvent, using cobalt acetate (or manganese acetate) and bromide as catalysts, using paraldehyde as an oxidation accelerator, at a temperature of 100-130°C and a pressure of 3MPa , use air to perform one-step low-temperature oxidation, and the reaction product is washed with acetic acid and then dried to obtain the product terephthalic acid.
![]()
2. From paraxylene Oxidation, or obtained by ammonia oxidation of p-xylene to terephthalonitrile and then hydrolysis.
Purpose
Used in the manufacture of synthetic resins, synthetic fibers and plasticizers, etc. Used as chromatographic analysis reagents.
